Optometry Board Part 1 Test #2 - Morning Session (Practice)
Next
0 of 175 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
Information
|
Optometry Board Practice Test for the NBEO® Part 1 Full Length Test #2 – Morning Session This test is comprised of 175 items. This is PRACTICE mode. There is no countdown timer and answers are shown after each question. |
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Exam is loading ...
You must sign in or sign up to start the exam.
You have to finish following exam, to start this exam:
Results
0 of 175 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You answered 0 of 0 (0) questions correct
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- Biochemistry 0%
- General Pharmacology: Anti-Inflammatory Drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: Anticoagulants 0%
- General Pharmacology: Antidepressants 0%
- General Pharmacology: Antifungal Drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: Antihistamine Drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: Antimicrobial Drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: Autonomic drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: Cardiovascular Drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: CNS Drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: Endocrine Drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: Gastrointestinal Drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: Hypertensive Drugs 0%
- General Pharmacology: Respiratory Drugs 0%
- Gross Anatomy: Blood Supply 0%
- Gross Anatomy: Brain/Nervous System 0%
- Gross Anatomy: Lymphatics 0%
- Gross Physiology: Kidney 0%
- Gross Physiology: Muscles 0%
- Gross Physiology: Pancreas 0%
- Gross Physiology: Pulmonary 0%
- Histology + Ocular Anatomy 0%
- Immunology + Systemic Disease: Immunopathology 0%
- Immunology: Systemic Health 0%
- Microbiology 0%
- Neuroanatomy 0%
- Neuroscience: Neuroanatomy 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Adnexa/Orbit 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Conjunctiva + Orbit 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Cornea 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Eyelid 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Iris 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Lens 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Ocular and Orbital Nerves 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Optic Nerve 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Orbit 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Orbit/Blood Supply 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Orbit/Extraocular Muscles 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Retina 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Uvea 0%
- Ocular Anatomy: Vitreous 0%
- Ocular and General Pharmacology 0%
- Ocular Disease: Conjunctiva 0%
- Ocular Disease: Cornea 0%
- Ocular Disease: Cornea/Refractive Surgery 0%
- Ocular Disease: Episclera/Sclera/Anterior and Posterior Uvea 0%
- Ocular Disease: Glaucoma 0%
- Ocular Disease: Lens/Cataract/IOL Pre- and Post-op Care 0%
- Ocular Disease: Lids/Lashes/Lacrimal System 0%
- Ocular Disease: Neuro-Ophthalmic Disorder 0%
- Ocular Disease: Ocular Adnexa/Orbit/External Disease 0%
- Ocular Disease: Retina/Choroid 0%
- Ocular Disease: Trauma 0%
- Ocular Embryology and Development 0%
- Ocular Motility + Binocular Vision 0%
- Ocular Motility + Binocular Vision: Accommodation 0%
- Ocular Motility + Binocular Vision: Amblyopia 0%
- Ocular Motility + Binocular Vision: Ametropia 0%
- Ocular Motility + Binocular Vision: Fixation Disparity 0%
- Ocular Motility + Binocular Vision: Ocular Development 0%
- Ocular Motility + Binocular Vision: Ocular Motor Dysfunction 0%
- Ocular Motility + Binocular Vision: Vergence/OMD 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Anti-Inflammatory Agents 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Anti-Inflammatory Drugs 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Antihistamines 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Antimicrobial Drugs 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Autonomic Drugs 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Glaucoma Agents 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Glaucoma Drugs 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Preservatives 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Topical Anesthetics Drugs 0%
- Ocular Pharmacology: Topical Ocular Anesthetics 0%
- Ocular Physiology: Aqueous 0%
- Ocular Physiology: Cornea 0%
- Ocular Physiology: Neuroanatomy 0%
- Ocular Physiology: Tears 0%
- Ophthalmic Optics 0%
- Ophthalmic Optics: Lasers 0%
- Optics: Contact Lenses 0%
- Optics: Low Vision 0%
- Pharmacology 0%
- Systemic Disease: Autoimmune Disease 0%
- Systemic Disease: Demyelinating Disease 0%
- Systemic Disease: Endocrine System 0%
- Systemic Disease: Gastrointestinal System 0%
- Systemic Disease: Genetic Disease 0%
- Systemic Disease: Genetic Disorder 0%
- Systemic Disease: Genetic Disorders 0%
- Systemic Disease: Immunopathology 0%
- Systemic Disease: Inflammatory Disease 0%
- Systemic Disease: Neuroanatomy 0%
- Systemic Disease: Vasculitis Disorders 0%
- Visual Perception 0%
-
Based on your performance on this Optometry Board Part 1 Practice Test, you’re not yet ready for the NBEO® Part 1.
Keep your head up! Also, don’t focus on your estimated score, they mean essentially nothing at the start. Rarely does anyone start these exams and score well immediately, if that was the case then they wouldn’t even need to practice! These are ‘practice’ tests, meaning you’re practicing to improve your skills. If you continue to work hard and study, read and understand the solutions, practice with “OptometryBoards.com” daily and give it your best effort, we promise your score will improve. Review and learn for now, and the scores will come.
-The “OptometryBoards.com” Team
-
Congratulations! Based on your performance on this Optometry Board Part 1 Practice Test, you’re predicted to pass your NBEO® Part 1! Keep hammering away at our Optometry Board questions so that you can keep up the great work!
-The “OptometryBoards.com” Team
-
Question 1 of 175
1. Question
Patient comes in asking about wavefront- Guided Lasik. What are the benefits that this specific treatment provides compared to normal Lasik?
CorrectA. Wavefront provides less low level aberrations thus allowing the patient to achieve 20/20 without spectacle correction
IncorrectA. Wavefront provides less low level aberrations thus allowing the patient to achieve 20/20 without spectacle correction
-
Question 2 of 175
2. Question
Which of the following is the least appropriate illumination when testing color vision?
CorrectD. Standard fluorescent lighting
IncorrectD. Standard fluorescent lighting
-
Question 3 of 175
3. Question
Mr. Johnson visited his local optometrist for a follow up visit. He was diagnosed with uveitis, and was given a topical steroid on his first visit. The bottle containing Mr. Johnson’s medication will most likely be what color?
CorrectE. Pink cap indicates steroids. Red cap is mydriatic. Blue and yellow caps are glaucoma drugs.
IncorrectE. Pink cap indicates steroids. Red cap is mydriatic. Blue and yellow caps are glaucoma drugs.
-
Question 4 of 175
4. Question
If the objective angle of deviation in esotropia is 35 degrees and the angle of anomaly is 45 degrees esotropia, what form of correspondence has a patient in the absence of diplopia?
CorrectA. Paradoxical type 1 anomalous retinal correspondence. harmonious ARC, the objective angle is equal to the subjective angle. In unharmonious ARC, the subjective angle is less than the objective angle. If the localization of the subjective and objective angles is crossed or uncrossed it is called paradoxical ARC. paradoxical type 1 is when the angle of anomaly is greater than the objective angle. Paradoxical type 2 is when the objective deviation is less than the subjective deviation.
IncorrectA. Paradoxical type 1 anomalous retinal correspondence. harmonious ARC, the objective angle is equal to the subjective angle. In unharmonious ARC, the subjective angle is less than the objective angle. If the localization of the subjective and objective angles is crossed or uncrossed it is called paradoxical ARC. paradoxical type 1 is when the angle of anomaly is greater than the objective angle. Paradoxical type 2 is when the objective deviation is less than the subjective deviation.
-
Question 5 of 175
5. Question
Which of the following is TRUE regarding Scleral chemical acid injury?
CorrectA. Acids = Coagulation/denaturation/precipitation of proteins. Alkali = Saponification of fatty acids within cell membranes
IncorrectA. Acids = Coagulation/denaturation/precipitation of proteins. Alkali = Saponification of fatty acids within cell membranes
-
Question 6 of 175
6. Question
When performing park’s 3 steps in your patient, you find the following: Left hypertropia in primary position, hyperopia increase in dextroversion and hypertropia increased in right head tilt. According to this information, which one of the following should be the affected muscle?
CorrectC. RSR. When performing Park’s 3 step we are only concerned with the muscle that makes the deviation WORSE not better. A left hypertrophia muscles affected are either the right IR, SO or left SR, IO.
IncorrectC. RSR. When performing Park’s 3 step we are only concerned with the muscle that makes the deviation WORSE not better. A left hypertrophia muscles affected are either the right IR, SO or left SR, IO.
-
Question 7 of 175
7. Question
Which of the following are not functions of the tear film?
CorrectD. The glands of wolfring are located in the tarsal conjunctiva and are assistant lacrimal glands along with the glands of Kruse that provide aqueous layer to the tear film.
IncorrectD. The glands of wolfring are located in the tarsal conjunctiva and are assistant lacrimal glands along with the glands of Kruse that provide aqueous layer to the tear film.
-
Question 8 of 175
8. Question
Which ophthalmic spectacle aberration is related to Petzval curvature?
CorrectF. Curvature of the field.
IncorrectF. Curvature of the field.
-
Question 9 of 175
9. Question
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Aniridia?
CorrectE. Aniridia is a loss or lack of iris. Synechia will only present when an iris is present.
IncorrectE. Aniridia is a loss or lack of iris. Synechia will only present when an iris is present.
-
Question 10 of 175
10. Question
Out of the following statements, select the one answer that is NOT true regarding telescopes.
CorrectC.
IncorrectC.
-
Question 11 of 175
11. Question
An ocular lens +4.00 +1.00 x180 is ground in minus cylinder form with the flattest of the two back surfaces having a power of -3.00 D. What is the base curve?
CorrectC. +8.00
Don’t let the plus cyl format fool you. Transpose this power into minus cyl form = +5.00 – 1.00 x 090. In minus cyl format, the base curve is the most plus curve. In plus cyl format, the base curve is the most minus curve. The flatter of the two meridians is the most plus of the two.
The base curve is the front surface of the lens and gives the lens its shape.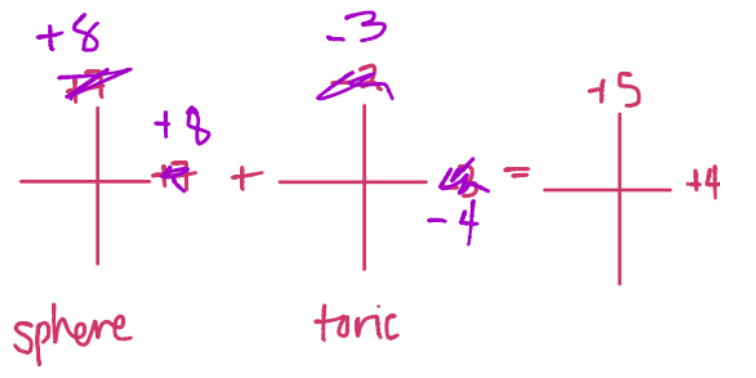 Incorrect
IncorrectC. +8.00
Don’t let the plus cyl format fool you. Transpose this power into minus cyl form = +5.00 – 1.00 x 090. In minus cyl format, the base curve is the most plus curve. In plus cyl format, the base curve is the most minus curve. The flatter of the two meridians is the most plus of the two.
The base curve is the front surface of the lens and gives the lens its shape.
-
Question 12 of 175
12. Question
Which of the following is accurate for patients who has a central corneal nebula?
CorrectC. Nebular corneal opacity is a faint opacity which results due to superficial scars involving Bowman’s layer and superficial stroma.
IncorrectC. Nebular corneal opacity is a faint opacity which results due to superficial scars involving Bowman’s layer and superficial stroma.
-
Question 13 of 175
13. Question
What is the perceptual/developmental experience of fusion of dichoptic images with similar but contrast-reversed targets that fall on corresponding retinal loci?
CorrectA. Confusion. Occurs when very different images are formed simultaneously on corresponding retinal points in the two eyes. Diplopia occurs when different images are formed simultaneously on non-corresponding retinal points in the two eyes.
IncorrectA. Confusion. Occurs when very different images are formed simultaneously on corresponding retinal points in the two eyes. Diplopia occurs when different images are formed simultaneously on non-corresponding retinal points in the two eyes.
-
Question 14 of 175
14. Question
Cholesterol is the primary component of what type of secretory cell?
CorrectD. Meibomian gland. Goblet cells secrete mucus, moll and wolfring secrete aqueous layer
IncorrectD. Meibomian gland. Goblet cells secrete mucus, moll and wolfring secrete aqueous layer
-
Question 15 of 175
15. Question
What area of the eye has the lowest concentration of GAGs?
CorrectD. Sclera contains the lowest level of GAGs in the eye. The cornea, particularly the stroma of the cornea, contains the highest level of GAGs in the eye
IncorrectD. Sclera contains the lowest level of GAGs in the eye. The cornea, particularly the stroma of the cornea, contains the highest level of GAGs in the eye
-
Question 16 of 175
16. Question
An astigmatic reduced eye has a power of +60 D @ 090 and +58 D @ 180 with standard axial length. What is the ocular refraction?
CorrectB. +2.00-2.00X180 without doing any math we know there is 2.00D of cylinder on this patient. So options A and D are eliminated. WTH astigmatism means there is more power on the 090 corneal axis. ATH astigmatism means there is more power on the 180 corneal axis. In this case the higher power is on the 090 so the patient is WTH astigmatism. The standard plano power of an eye is 60D so the 090 axis will have plano power and -2.00 on the 180 axis.
IncorrectB. +2.00-2.00X180 without doing any math we know there is 2.00D of cylinder on this patient. So options A and D are eliminated. WTH astigmatism means there is more power on the 090 corneal axis. ATH astigmatism means there is more power on the 180 corneal axis. In this case the higher power is on the 090 so the patient is WTH astigmatism. The standard plano power of an eye is 60D so the 090 axis will have plano power and -2.00 on the 180 axis.
-
Question 17 of 175
17. Question
Which is the most prevalent color vision anomaly in males?
CorrectC. Deuteranomaly
IncorrectC. Deuteranomaly
-
Question 18 of 175
18. Question
You are performing duochrome test in the refraction. The lens placed in the phoropter at the beginning of the test is a -4.00 DS lens. If the patient reports seeing the letters on the green side darker and better than the red side; what does this mean?
CorrectB. RAM GAP. Red add minus because the lens is over plused or under minused. Green add plus because the lens is under plused or over minused
IncorrectB. RAM GAP. Red add minus because the lens is over plused or under minused. Green add plus because the lens is under plused or over minused
-
Question 19 of 175
19. Question
Vertical imbalance must be corrected for reading level 10 mm below the distance OC for the following prescription:
OD: -1.00-2.00×180
OS: -1.00-3.00×180
Add: +2.00
Segment drop of 5mmWhich of the following segment drops would allow for a drop of 5 mm?
CorrectD. FT28 has a seg drop of 5mm. FT40 has a seg drop of 20. Round 22 has a seg drop of 11 mm Round 38 has a seg drop of 19 mm
IncorrectD. FT28 has a seg drop of 5mm. FT40 has a seg drop of 20. Round 22 has a seg drop of 11 mm Round 38 has a seg drop of 19 mm
-
Question 20 of 175
20. Question
When performing direct ophthalmoscopy which of the following is true?
CorrectC. Direct is erect and INdirect is INverted. Remember this mnemonic and you will get these questions right every time.
IncorrectC. Direct is erect and INdirect is INverted. Remember this mnemonic and you will get these questions right every time.
-
Question 21 of 175
21. Question
What is the latency for optokinetic nystagmus reflex?
CorrectC. 140 millisec: Vestibulo ocular nystagmus is 16 millisec, and OKN is 140 millisec
IncorrectC. 140 millisec: Vestibulo ocular nystagmus is 16 millisec, and OKN is 140 millisec
-
Question 22 of 175
22. Question
What type of astigmatism would a patient with soft contact lens prescription of : -2.00+2.00×100 have?
CorrectB. Simple myopic with the rule
IncorrectB. Simple myopic with the rule
-
Question 23 of 175
23. Question
Patient presents with the following topography. What layer of the cornea is most affected based off what you see?
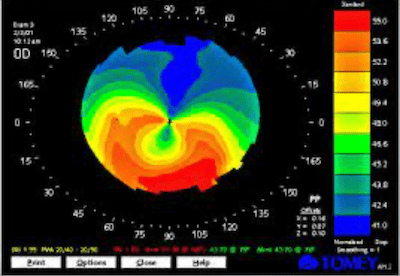 Correct
CorrectC. Corneal stroma thinning is affected in both Keratoconus and PMN. Note on the topography the red indicated corneal steeping and blue is corneal flattening.
IncorrectC. Corneal stroma thinning is affected in both Keratoconus and PMN. Note on the topography the red indicated corneal steeping and blue is corneal flattening.
-
Question 24 of 175
24. Question
A lens clock reads as follows on its major meridians: 160 degree meridian front surface +4.00 D, back surface -6.00 D 70 degree meridian; front surface +4.00 D, back surface -8.00 D. Assuming the lens material has an index of 1.53, what is the approximate prescription (nominal) in PLUS cylinder form?
CorrectD.
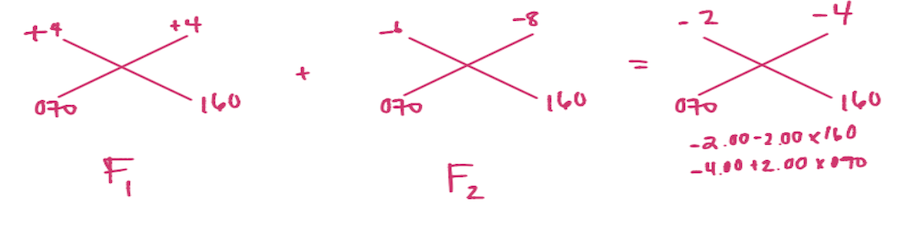 Incorrect
IncorrectD.
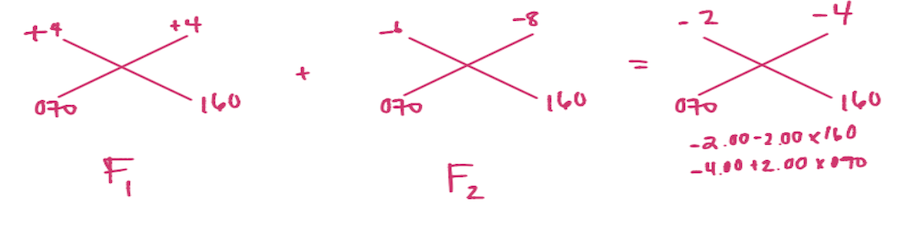
-
Question 25 of 175
25. Question
What term best describes the reflex eye movement that is seen following the termination of a barany chair clockwise stimulation in the dark?
CorrectB. Post rotational nystagmus. OKAN describes the reflex eye movement that is seen after the stoppage of a barany chair stimulation in ambient room lighting that is enriched with objects.
IncorrectB. Post rotational nystagmus. OKAN describes the reflex eye movement that is seen after the stoppage of a barany chair stimulation in ambient room lighting that is enriched with objects.
-
Question 26 of 175
26. Question
Which condition can present with unilateral anterior uveitis?
CorrectC. Posner Schlossman Syndrome, also known as glaucomatocyclitis crisis, presents as an acute unilateral nongranulomatous anterior uveitis due to inflammation in the trabecular meshwork. These episodes are recurring and self-limiting each time and with the slit lamp biomicroscope, the practitioner will be able to see fine keratic precipitates. In addition herpes and Fuch’s Heterochromic Iridocyclitis result in a unilateral chronic non-granulomatous anterior uveitis.
Any type of systemic condition would result in a bilateral uveitis. Keep in mind the ones to cause a chronic granulomatous anterior uveitis include sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, syphilis, lyme disease and herpes amongst others. All five of these conditions may also result in a panuveitis and/or posterior uveitis.
IncorrectC. Posner Schlossman Syndrome, also known as glaucomatocyclitis crisis, presents as an acute unilateral nongranulomatous anterior uveitis due to inflammation in the trabecular meshwork. These episodes are recurring and self-limiting each time and with the slit lamp biomicroscope, the practitioner will be able to see fine keratic precipitates. In addition herpes and Fuch’s Heterochromic Iridocyclitis result in a unilateral chronic non-granulomatous anterior uveitis.
Any type of systemic condition would result in a bilateral uveitis. Keep in mind the ones to cause a chronic granulomatous anterior uveitis include sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, syphilis, lyme disease and herpes amongst others. All five of these conditions may also result in a panuveitis and/or posterior uveitis.
-
Question 27 of 175
27. Question
Please select the correct order of ear bones from most superficial to least superficial.
CorrectB. Malleus, incus, stapes
IncorrectB. Malleus, incus, stapes
-
Question 28 of 175
28. Question
A microscope has a 6mm focal length objective and 16mm focal length ocular lens. The separation between the two lenses is 150mm. Calculate the Total angular magnification of the microscope.
CorrectD. 332X
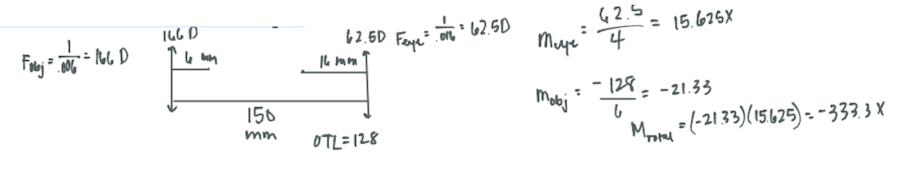 Incorrect
IncorrectD. 332X
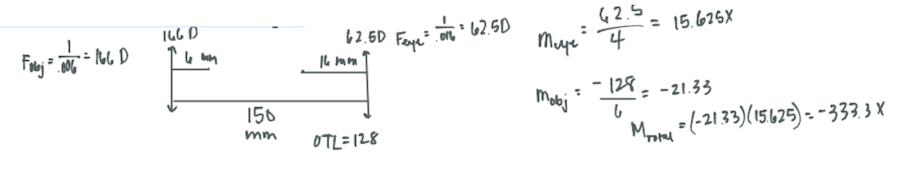
-
Question 29 of 175
29. Question
Given an entrance pupil with diameter 75 mm and exit pupil diameter 6.3 mm, what is the total length of the a keplerian telescope which has an objective +1.25D lens
CorrectC. 867 mm
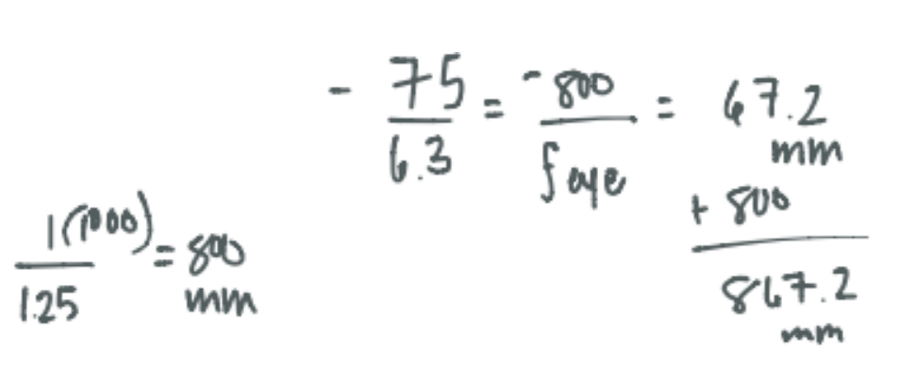 Incorrect
IncorrectC. 867 mm
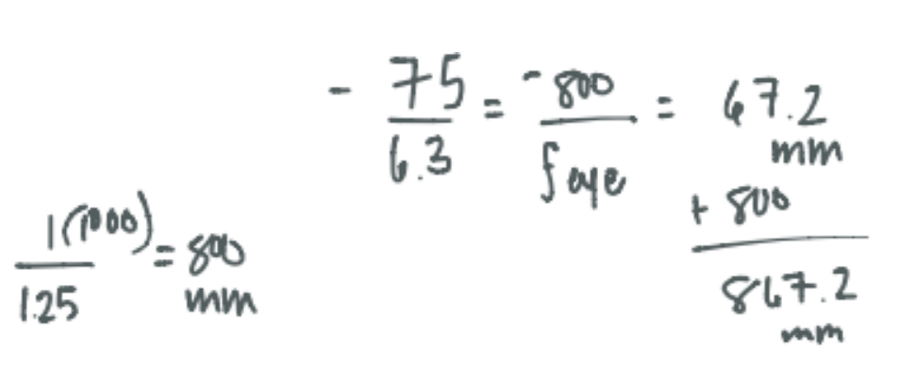
-
Question 30 of 175
30. Question
What is considered the average IOP value in a healthy patient younger than 50?
CorrectC. 15.5 mm Hg is the average IOP found in non glaucoma patients under the age of 50.
IncorrectC. 15.5 mm Hg is the average IOP found in non glaucoma patients under the age of 50.
-
Question 31 of 175
31. Question
What structure provides neurological support to the central nervous system?
CorrectA. Oligodendrocytes are the myelinating cells of the CNS that enable fast saltatory impulse propagation. Schwann Cells are myelinating cells of the PNS that provide the same function of the Oligodendrocytes but only to the PNS. Altho oligodendrocytes are a type of glial cells, the answer is not specific to only the CNS. Astrocytes are a sub type of glial cell that are star shaped and process envelope synapse made by the neuron.
IncorrectA. Oligodendrocytes are the myelinating cells of the CNS that enable fast saltatory impulse propagation. Schwann Cells are myelinating cells of the PNS that provide the same function of the Oligodendrocytes but only to the PNS. Altho oligodendrocytes are a type of glial cells, the answer is not specific to only the CNS. Astrocytes are a sub type of glial cell that are star shaped and process envelope synapse made by the neuron.
-
Question 32 of 175
32. Question
Which of the following does not affect accommodative response?
CorrectE. All of the above affect the response
IncorrectE. All of the above affect the response
-
Question 33 of 175
33. Question
What mydriatic agent is used to treat motion sickness?
CorrectC. scopolamine is the go to drug for motion sickness
IncorrectC. scopolamine is the go to drug for motion sickness
-
Question 34 of 175
34. Question
While doing retinoscopy neutralize the 045 meridian with +6.00D lens at 40 cm. You then neutralize the 135 meridian with a +4.25 D lens at 67 cm. What is the prescription you would prescribe to this patient?
CorrectC.
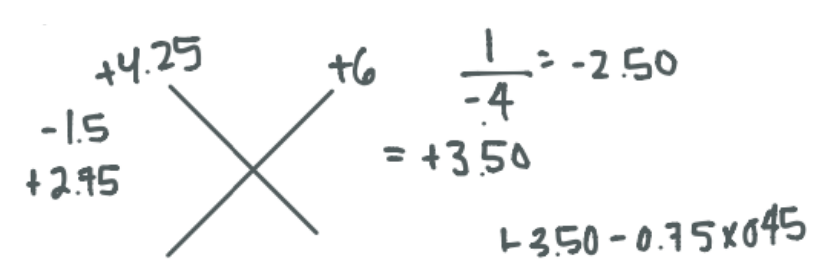 Incorrect
IncorrectC.
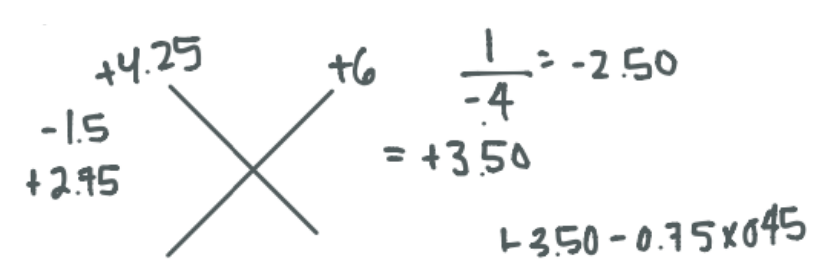
-
Question 35 of 175
35. Question
Which of the following are not considered signs of keratoconus? (SELECT 3)
CorrectB,E,G. Ferry’s line is corneal epithelial iron deposits, Stocker’s line is caused by pterygium, Kayser- fleischer ring is caused by wilson’s disease
IncorrectB,E,G. Ferry’s line is corneal epithelial iron deposits, Stocker’s line is caused by pterygium, Kayser- fleischer ring is caused by wilson’s disease
-
Question 36 of 175
36. Question
You perform Hirschberg test on a patient and the test reveals: OD is centered and OS -1.5mm. What is the magnitude?
CorrectA. 1.5mm x 22=33PD
IncorrectA. 1.5mm x 22=33PD
-
Question 37 of 175
37. Question
You measure an Rx of +4.50-6.00×075 in a lensometer with a +25D standard badal lens. How far does the object move from its original primary position on the 165 meridian?
CorrectB. 2.4 further. -1.50=x25^2 x=-2.4mm
IncorrectB. 2.4 further. -1.50=x25^2 x=-2.4mm
-
Question 38 of 175
38. Question
A lens has a power of pl -2.00×090 it is decentered 2 mm nasally and edged 50 mm round. Which edge is the thickest?
CorrectC. Temporal. Plus lenses are thicker in the center. Minus lenses are thicker in the periphery. Draw the lens in a lens cross with this key in mind.
IncorrectC. Temporal. Plus lenses are thicker in the center. Minus lenses are thicker in the periphery. Draw the lens in a lens cross with this key in mind.
-
Question 39 of 175
39. Question
The mass of tissue localized between the sternum, vertebral column and the lungs is known as.
CorrectD. The mediastinum is a space in the thorax that contains a group of organs, vessels, nerves, lymphatics and their surrounding connective tissue. It lies in the midline of the chest between the pleura of each lung and extends from the sternum to the vertebral column
IncorrectD. The mediastinum is a space in the thorax that contains a group of organs, vessels, nerves, lymphatics and their surrounding connective tissue. It lies in the midline of the chest between the pleura of each lung and extends from the sternum to the vertebral column
-
Question 40 of 175
40. Question
An optometrist has reduced the size of his projected chart to correspond to a testing distance of 15 ft. A patient needs to be 5 ft in front of the chart to be able to read the 20/400 letter. What is the actual acuity of this patient? (SELECT 3)
CorrectA.D.F. (15/5)(400)=20/1200=6/x
IncorrectA.D.F. (15/5)(400)=20/1200=6/x
-
Question 41 of 175
41. Question
A patient is a 3D uncorrected hyperopia and examiner is an 3D uncorrected myope. Assuming accommodation fully relaxed on the examiner and patient, what lens should be used in the peephole of the direct ophthalmoscope to view the fundus?
CorrectD. +3+-3=0D
IncorrectD. +3+-3=0D
-
Question 42 of 175
42. Question
A 53 year old female presents to the clinic with bloody sputum, fatigue, and a chest x-ray which shows multiple light areas of varying size leading you to suspect a diagnosis of tuberculosis. After culturing, which of the following stains would you expect to be positive?
CorrectD. Acid fast staining
The pathogen causing tuberculosis is mycobacterium tuberculosis. The structure of this bacteria includes mycolic acid and a key characteristic of these long fatty acids is that it resists gram staining. Rose Bengal stains borders of herpes simplex and also aids in visualizing dead devitalized cells in the conjunctiva & cornea.IncorrectD. Acid fast staining
The pathogen causing tuberculosis is mycobacterium tuberculosis. The structure of this bacteria includes mycolic acid and a key characteristic of these long fatty acids is that it resists gram staining. Rose Bengal stains borders of herpes simplex and also aids in visualizing dead devitalized cells in the conjunctiva & cornea. -
Question 43 of 175
43. Question
What cholinergic antagonist reaches maximum mydriasis the fastest?
CorrectC. Scopolamine. Scopolamine reaches maximum mydriasis the fastest due to the fact that it crosses the blood brain barrier
IncorrectC. Scopolamine. Scopolamine reaches maximum mydriasis the fastest due to the fact that it crosses the blood brain barrier
-
Question 44 of 175
44. Question
Where does blood filtration occur in the nephron of a kidney?
CorrectD. Glomerulus. Blood is filtered at the glomerular capillaries. Water and solutes are filtered to the glomerular capsule.
IncorrectD. Glomerulus. Blood is filtered at the glomerular capillaries. Water and solutes are filtered to the glomerular capsule.
-
Question 45 of 175
45. Question
A 25 y/o male is allergic to penicillin but requires antibacterial treatment with a drug that has a similar spectrum of coverage. Which of the following should be prescribed?
CorrectB. Erythromycin.
IncorrectB. Erythromycin.
-
Question 46 of 175
46. Question
Which of the following is not a non-strabismic anomaly? (SELECT 2)
CorrectA,D. Non-Strabismic are visual disorders that affect the subject’s binocular vision and visual performance, especially when performing tasks requiring near vision. They occur when the accommodative and/or vergence response of the visual system is defective. Strabismus is usually unilateral condition or tropia
IncorrectA,D. Non-Strabismic are visual disorders that affect the subject’s binocular vision and visual performance, especially when performing tasks requiring near vision. They occur when the accommodative and/or vergence response of the visual system is defective. Strabismus is usually unilateral condition or tropia
-
Question 47 of 175
47. Question
What layer of the retina does the photoreceptor body found in?
CorrectA. ONL. The photoreceptor receives its signal from the RPE so the OS portion of the photoreceptor is like a dendrite and collects the photon. Interpretation occurs where a nucleus is present. ONL is the first layer of nuclear location in the retina.
IncorrectA. ONL. The photoreceptor receives its signal from the RPE so the OS portion of the photoreceptor is like a dendrite and collects the photon. Interpretation occurs where a nucleus is present. ONL is the first layer of nuclear location in the retina.
-
Question 48 of 175
48. Question
You perform duochrome and ask your patient which side is more clear; and patient says that both sides are equal. What could be the problem?
CorrectD. Room illumination. Room illumination is important when doing duochrome. If the illumination is too bright then you can cause a pinhole effect on the patient thus creating a false reading.
IncorrectD. Room illumination. Room illumination is important when doing duochrome. If the illumination is too bright then you can cause a pinhole effect on the patient thus creating a false reading.
-
Question 49 of 175
49. Question
The intrinsic ability of muscle tissue to return to its original shape best defines
CorrectA. Elasticity. Extensibility: the ability to be extended or stretched. Compliance the property of a material undergoing elastic deformation or (of a gas) change in volume when subjected to an applied force. Contractility is the ability of muscle cells to forcefully shorten.
IncorrectA. Elasticity. Extensibility: the ability to be extended or stretched. Compliance the property of a material undergoing elastic deformation or (of a gas) change in volume when subjected to an applied force. Contractility is the ability of muscle cells to forcefully shorten.
-
Question 50 of 175
50. Question
Which part of the ear is controlled by linear VOR?
CorrectC. Vestibule is controlled by linear VOR. Semicircular canals are controlled by angular VOR
IncorrectC. Vestibule is controlled by linear VOR. Semicircular canals are controlled by angular VOR
-
Question 51 of 175
51. Question
During the event identified by number 2, which of the following molecular events is occurring?
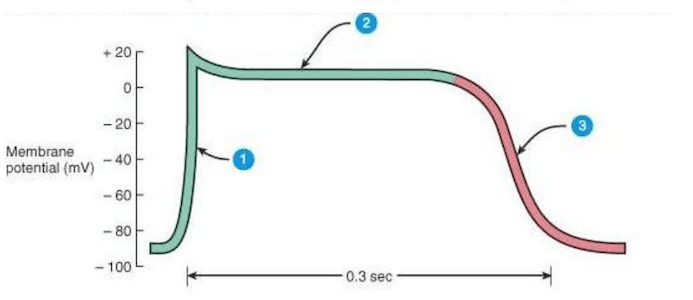 Correct
CorrectB. 1) opening of Na+ channels 2) opening of calcium channels 3) Calcium channels inactivated and potassium flow out
IncorrectB. 1) opening of Na+ channels 2) opening of calcium channels 3) Calcium channels inactivated and potassium flow out
-
Question 52 of 175
52. Question
Parathyroid hormone, calcitriol and calcitonin are
CorrectC. Main regulators of calcium in the blood. Calcitonin is a hormone that your thyroid gland makes and releases to help regulate calcium levels in your blood by decreasing it. Calcitriol is used to treat and prevent low levels of calcium and bone disease in patients whose kidneys or parathyroid glands. Parathyroid Hormone stimulates release of calcitonin from the parathyroid glands.
IncorrectC. Main regulators of calcium in the blood. Calcitonin is a hormone that your thyroid gland makes and releases to help regulate calcium levels in your blood by decreasing it. Calcitriol is used to treat and prevent low levels of calcium and bone disease in patients whose kidneys or parathyroid glands. Parathyroid Hormone stimulates release of calcitonin from the parathyroid glands.
-
Question 53 of 175
53. Question
Young male patient presents to your office with anisocoria. After examination, you find the following: Anisocoria is larger in dim illumination and accommodative response is increased. According to the information, which one of the following is the MOST probable cause of pupillary anomaly?
CorrectA. Horner’s syndrome. Patients pupils will have anisocoria with the ptotic eye having the smaller pupil. The anisocoria is more prominent in the dark, indicating pathology of the pupillary dilator. The smaller pupil takes a longer time to dilate when a bright source of light is moved away from the eye. This phenomenon is called dilation lag
IncorrectA. Horner’s syndrome. Patients pupils will have anisocoria with the ptotic eye having the smaller pupil. The anisocoria is more prominent in the dark, indicating pathology of the pupillary dilator. The smaller pupil takes a longer time to dilate when a bright source of light is moved away from the eye. This phenomenon is called dilation lag
-
Question 54 of 175
54. Question
Interstitial fluid is accumulated in all of the following sites, EXCEPT?
CorrectA. Cerebrospinal fluid. Interstitial fluid is fluid found within the space around a cell. It comes from blood vessel leakage. Cerebrospinal fluid is colorless fluid produced by the spinal cord that surrounds the CNS not space around cells.
IncorrectA. Cerebrospinal fluid. Interstitial fluid is fluid found within the space around a cell. It comes from blood vessel leakage. Cerebrospinal fluid is colorless fluid produced by the spinal cord that surrounds the CNS not space around cells.
-
Question 55 of 175
55. Question
Which of the following diagnostic tests is NEVER indicated in cases of scleral injury due to metal foreign body?
CorrectB. MRI. MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance imaging. Magnets and metal objects never work well together.
IncorrectB. MRI. MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance imaging. Magnets and metal objects never work well together.
-
Question 56 of 175
56. Question
A 1.53 index prism with an apical angle of 15 deg used at 25 cm, produces an image displacement of how much in cm?
CorrectA. 7.95 degrees ; d=A(n-a) -> d= 15(1.53-1)
IncorrectA. 7.95 degrees ; d=A(n-a) -> d= 15(1.53-1)
-
Question 57 of 175
57. Question
Which of the following will invariably lead to metabolic alkalosis if untreated?
CorrectD. Metabolic alkalosis is directly a result of too much alkaline in the blood or lack of acid in the body. Stomach acid is the greatest contributor to metabolic acid in the body. If constant vomiting occurs the body becomes more basic due to this amount of acidic loss.
IncorrectD. Metabolic alkalosis is directly a result of too much alkaline in the blood or lack of acid in the body. Stomach acid is the greatest contributor to metabolic acid in the body. If constant vomiting occurs the body becomes more basic due to this amount of acidic loss.
-
Question 58 of 175
58. Question
Which of the following is not associated with Krukenberg spindles? (SELECT 2)
CorrectB,D. Krukenberg spindles are associated with pigment loss of the iris. Iris transillumination and pigment dispersion syndrome are key indications of krukenberg spindles. Lens cataracts can cause some loss of pigment but are not a direct cause. Weiss’ ring is caused by trauma where the iris pressed up against the lens of the eye.
IncorrectB,D. Krukenberg spindles are associated with pigment loss of the iris. Iris transillumination and pigment dispersion syndrome are key indications of krukenberg spindles. Lens cataracts can cause some loss of pigment but are not a direct cause. Weiss’ ring is caused by trauma where the iris pressed up against the lens of the eye.
-
Question 59 of 175
59. Question
Using the picture please determine the letter that is consistent with bacterial resistance
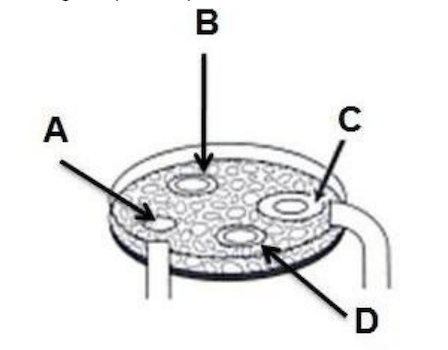 Correct
CorrectC. The smaller the zone of inhibition the more bacterial resistant a drug is. The larger the zone of inhibition the more effective a drug is on the bacterial
IncorrectC. The smaller the zone of inhibition the more bacterial resistant a drug is. The larger the zone of inhibition the more effective a drug is on the bacterial
-
Question 60 of 175
60. Question
This electrical event triggers contraction of the atria.
CorrectD. P wave. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart.
IncorrectD. P wave. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart.
-
Question 61 of 175
61. Question
Which of the following will invariably lead to metabolic alkalosis if untreated?
CorrectD. Vomiting. Metabolic alkalosis a disorder that elevates the serum bicarbonate, can result from several mechanisms: intracellular shift of hydrogen ions; gastrointestinal loss of hydrogen ions; excessive renal hydrogen ion loss; administration and retention of bicarbonate ions; or volume contraction.
IncorrectD. Vomiting. Metabolic alkalosis a disorder that elevates the serum bicarbonate, can result from several mechanisms: intracellular shift of hydrogen ions; gastrointestinal loss of hydrogen ions; excessive renal hydrogen ion loss; administration and retention of bicarbonate ions; or volume contraction.
-
Question 62 of 175
62. Question
What is the object height of a system where the inverted real +5 mm image is located 25 cm behind a +5D lens?
CorrectC. Real erect 1.25 mm object. Real objects create real images. We first have to find the object vergence ( L’=L+F ; (100/25)=L+(5)-> 4=L+5 -> L=-1 ; then we find the magnification of the system ; M= obj/img ; M=(-1/4)-> M= -0.25 ; M=obj/image ; 0.25=obj/5 -> 1.25 mm
IncorrectC. Real erect 1.25 mm object. Real objects create real images. We first have to find the object vergence ( L’=L+F ; (100/25)=L+(5)-> 4=L+5 -> L=-1 ; then we find the magnification of the system ; M= obj/img ; M=(-1/4)-> M= -0.25 ; M=obj/image ; 0.25=obj/5 -> 1.25 mm
-
Question 63 of 175
63. Question
Given the index the cornea to be 1.376 and index of the aqueous to be 1.336 of a schematic eye, what’s the complete equivalent power of the cornea when the distance between the front and back surfaces of the cornea is 0.5 mm (rfront= 7.7mm, rback= 6.8mm)
CorrectB.+43.056D
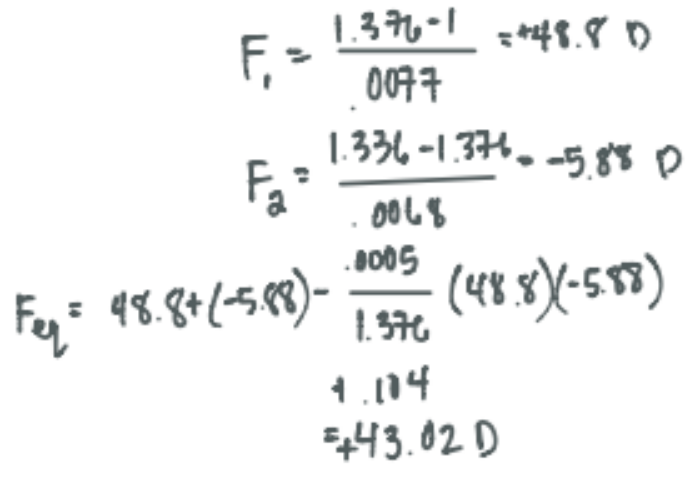 Incorrect
IncorrectB.+43.056D
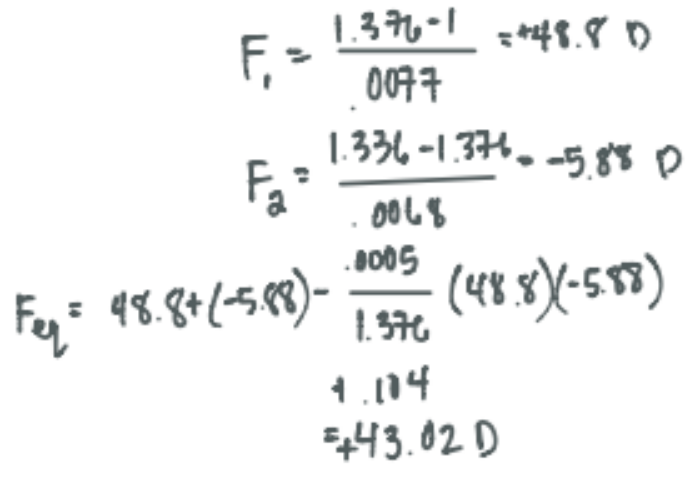
-
Question 64 of 175
64. Question
Which drug is used to treat hyperthyroidism? (SELECT TWO)
CorrectB and E. Propylthiouracil and methimazole
→ Propylthiouracil blocks the synthesis of thyroid hormones by blocking peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 as well as blocking oxidation of iodine in the thyroid. Those with liver issues have to be careful as it carries a black box warning of hepatotoxicity.
→ Methimazole blocks the synthesis of thyroid hormones by blocking oxidation of iodine in the thyroid. Adverse effects include being teratogenic as well as agranulocytosis.
Levothyroxine, also known as Synthroid, is used for low thyroid levels (think Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis). Remember with low thyroid levels, we expect to see increased TSH and decreased T3 & T4 data in their bloodwork results.
Glyburide and Pioglitazone are both used for treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Glyburide is a sulfonylurea so careful utilizing it for patients with sensitivities to sulfa! Other sulfonylureas include chlorpropamide and glipizide and all of these block K+ channels on beta cells of the pancreas to promote insulin release.
Pioglitazone is a thiazolidinedione that acts on peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPAR-gamma) to increase insulin sensitivity.IncorrectB and E. Propylthiouracil and methimazole
→ Propylthiouracil blocks the synthesis of thyroid hormones by blocking peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 as well as blocking oxidation of iodine in the thyroid. Those with liver issues have to be careful as it carries a black box warning of hepatotoxicity.
→ Methimazole blocks the synthesis of thyroid hormones by blocking oxidation of iodine in the thyroid. Adverse effects include being teratogenic as well as agranulocytosis.
Levothyroxine, also known as Synthroid, is used for low thyroid levels (think Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis). Remember with low thyroid levels, we expect to see increased TSH and decreased T3 & T4 data in their bloodwork results.
Glyburide and Pioglitazone are both used for treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Glyburide is a sulfonylurea so careful utilizing it for patients with sensitivities to sulfa! Other sulfonylureas include chlorpropamide and glipizide and all of these block K+ channels on beta cells of the pancreas to promote insulin release.
Pioglitazone is a thiazolidinedione that acts on peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPAR-gamma) to increase insulin sensitivity. -
Question 65 of 175
65. Question
While working on a lensometer with a standard +25D badal lens, you moved the dial 5mm closer to the badal. You see a clear neutral target in the lensometer, what is the back surface power of the lens? How many mm of movement correspond to 1D?
CorrectC. +3.125D, 1.6mm
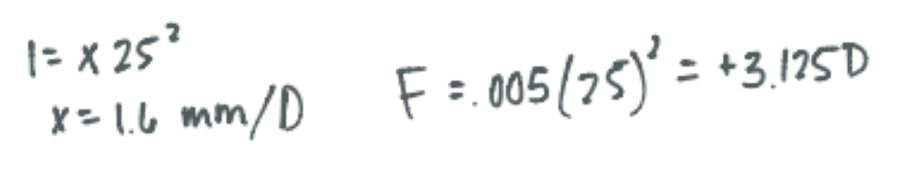 Incorrect
IncorrectC. +3.125D, 1.6mm
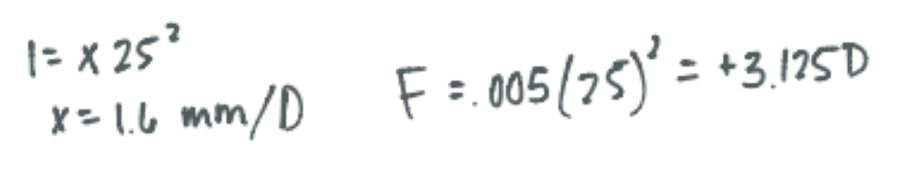
-
Question 66 of 175
66. Question
Which of the following are controlled by the autonomic nervous system? (SELECT TWO)
CorrectC and D. The autonomic nervous system is composed of neurons that control input of the visceral organs, secretory glands, and smooth muscles. However, the autonomic nervous system is not a voluntary input system. Such examples of these would be the first two options listed.
IncorrectC and D. The autonomic nervous system is composed of neurons that control input of the visceral organs, secretory glands, and smooth muscles. However, the autonomic nervous system is not a voluntary input system. Such examples of these would be the first two options listed.
-
Question 67 of 175
67. Question
Which of the following are located on the lateral wall of the orbit?
CorrectA. Greater wing of sphenoid. Great Z is a lateral play, Front Less, SMEL medial, My Pal Get’s Z on the floor
IncorrectA. Greater wing of sphenoid. Great Z is a lateral play, Front Less, SMEL medial, My Pal Get’s Z on the floor
-
Question 68 of 175
68. Question
The line within panum’s space that connects the set of spatial points in space that are perceived as single while binocularly fixating on an object point is called?
CorrectB. horopter.
IncorrectB. horopter.
-
Question 69 of 175
69. Question
Which of the following is the major hormone that regulates water loss?
CorrectD. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) helps regulate the amount of water in your body. It works to control the amount of water your kidneys reabsorb as they filter out waste from your blood. This hormone is also called arginine vasopressin
IncorrectD. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) helps regulate the amount of water in your body. It works to control the amount of water your kidneys reabsorb as they filter out waste from your blood. This hormone is also called arginine vasopressin
-
Question 70 of 175
70. Question
Which of the following structures is considered the pacemaker of the heart?
CorrectA. SA node is the start node.
IncorrectA. SA node is the start node.
-
Question 71 of 175
71. Question
When your patient is doing a left head tilt, the respective action of the left inferior rectus and the right superior rectus can be explained by the following principle
CorrectA. Sherrington’s law of innervation is concerned with the contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the same eye. Hering’s law is the muscle innervation between 2 eyes. Remember sherring the same eye.
IncorrectA. Sherrington’s law of innervation is concerned with the contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the same eye. Hering’s law is the muscle innervation between 2 eyes. Remember sherring the same eye.
-
Question 72 of 175
72. Question
If the Buccinator muscle is damaged, then which gland would be impacted?
CorrectC. Parotid gland. The human parotid duct (Stensen’s duct) is a single duct arising from the anterior border of the parotid gland. In adults, the parotid duct is about 6–8 cm long. It crosses the masseter muscle and turns medially at almost a right angle to traverse the buccal fat pad and buccinator muscle.
IncorrectC. Parotid gland. The human parotid duct (Stensen’s duct) is a single duct arising from the anterior border of the parotid gland. In adults, the parotid duct is about 6–8 cm long. It crosses the masseter muscle and turns medially at almost a right angle to traverse the buccal fat pad and buccinator muscle.
-
Question 73 of 175
73. Question
Which of the following diagnostic non contact lenses provides an erect virtual image of the fundus?
CorrectB. Hruby lens
IncorrectB. Hruby lens
-
Question 74 of 175
74. Question
The apical surfaces of the fetal nucleus form
CorrectB. Upright Y suture. The embryonic nucleus has no sutures. Sutures are only located in the fetal nucleus
IncorrectB. Upright Y suture. The embryonic nucleus has no sutures. Sutures are only located in the fetal nucleus
-
Question 75 of 175
75. Question
You perform near point of accommodation on a 2.00D myope wearing contact lens for full correction and determine it to be 8 cm in front of the cornea. What is his/her amplitude of accommodation?
CorrectC. 10.5D. 100/8=12.5D far point; Near point 2D. Aof A is near – far point : -12.5-2=10.5D
IncorrectC. 10.5D. 100/8=12.5D far point; Near point 2D. Aof A is near – far point : -12.5-2=10.5D
-
Question 76 of 175
76. Question
A reduced eye with index 1.333 is corrected with spectacle -5.25DS lens placed 12 mm in front of the eye. What is the power of this eye assuming standard axial length?
CorrectB. 67D ; (-5.25)/[1-(0.012)(-5.25)] = -4.93D; 1.333-1.000/-4.93= 67.54D
IncorrectB. 67D ; (-5.25)/[1-(0.012)(-5.25)] = -4.93D; 1.333-1.000/-4.93= 67.54D
-
Question 77 of 175
77. Question
Which of the following laboratory tests would be MOST appropriate for a patient with chronic, bilateral, granulomatous anterior uveitis?
CorrectA. Chest X-Ray. The patient is experiencing the signs of sarcoidosis. In addition we would run a ACE test
IncorrectA. Chest X-Ray. The patient is experiencing the signs of sarcoidosis. In addition we would run a ACE test
-
Question 78 of 175
78. Question
Select the letter with the correct sequence of structures that allows the normal sequence of excitation to progress through the heart.
CorrectD. SA is the start node-> AV node-> bundle of his -> purkinje fibers
IncorrectD. SA is the start node-> AV node-> bundle of his -> purkinje fibers
-
Question 79 of 175
79. Question
For a photochemical damage mechanism, which of the following is false characteristic?
CorrectD. will occur at any wavelength
IncorrectD. will occur at any wavelength
-
Question 80 of 175
80. Question
A 45 year old patient comes to your office with a chief complaint of blurry vision at distance at the end of the day. His current spectacle prescription has a back vertex power of -7.00 DS OD, OS with an add of +1.50 D. He explains he notices an improvement of symptoms if his spectacles are placed further from his eyes. According to his chief complaint and objective findings, the practitioner may expect what findings after finalizing the glasses prescription?
CorrectB. less myopia.
By increasing the vertex distance of the lenses, he is effectively inducing more plus power. Since the chief complaint is mainly for distance, we know presbyopia isn’t the best answer in this case as these patients have difficulties seeing at near. Given his age, its not a new finding since his habitual prescription has an add already built in.IncorrectB. less myopia.
By increasing the vertex distance of the lenses, he is effectively inducing more plus power. Since the chief complaint is mainly for distance, we know presbyopia isn’t the best answer in this case as these patients have difficulties seeing at near. Given his age, its not a new finding since his habitual prescription has an add already built in. -
Question 81 of 175
81. Question
Which of the following wavelengths of laser light is considered to be the MOST effective for the treatment of the macula but avoiding damage to the macula?
CorrectA. Further from blue, it is the safest (red)
IncorrectA. Further from blue, it is the safest (red)
-
Question 82 of 175
82. Question
You determined the near point of accommodation (push up method) to be 40 cm in front of point P when fully corrected. You repeated the NPA without correction and found it to be 67 cm in front of point P. Assuming full accommodation on both procedures; the amount and type of ametropia is?
CorrectC. 1D hyperopia. Patient FP vergence is -2.50D corrected. Patients FP vergence uncorrected is -1.50. Comparing the difference between these numbers will give you the total ametropia of the patient
IncorrectC. 1D hyperopia. Patient FP vergence is -2.50D corrected. Patients FP vergence uncorrected is -1.50. Comparing the difference between these numbers will give you the total ametropia of the patient
-
Question 83 of 175
83. Question
A patient with astigmatism was refracted at 10 mm and found the following spectacle correction; +2.50+2.50×180. Where are the far points located for this patient?
CorrectH. 19 and 39 cm behind the eye.
 Incorrect
IncorrectH. 19 and 39 cm behind the eye.

-
Question 84 of 175
84. Question
Which of the following lasers is highly used to treat recurrent corneal erosions?
CorrectA. Nd Yag
IncorrectA. Nd Yag
-
Question 85 of 175
85. Question
The portion of the kidney identified by letter B is called?
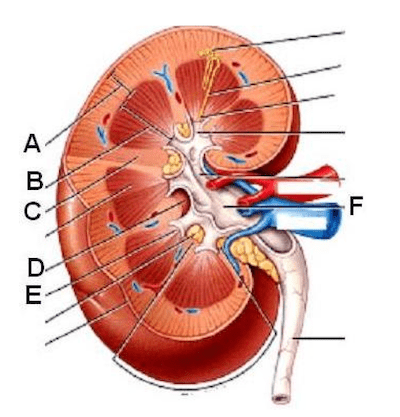 Correct
CorrectA. Renal Medulla. Renal pelvis is F. Renal column is B. Calyces is E
IncorrectA. Renal Medulla. Renal pelvis is F. Renal column is B. Calyces is E
-
Question 86 of 175
86. Question
The far point of a patient was determined to be a real object placed 50 cm from the eye’s principal point while wearing a +4.00DS contact lens. What amount and type of ametropia does the patient have?
CorrectB. 2D of hyperopia. Real object vergence is -2.00D hitting a +4.00D len . -2.00D-+4.00D=+2.00D
IncorrectB. 2D of hyperopia. Real object vergence is -2.00D hitting a +4.00D len . -2.00D-+4.00D=+2.00D
-
Question 87 of 175
87. Question
A 45 y/o patient with chronic liver disease is admitted to the general medicine ward due to upper gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to active peptic ulcer disease. Which of the following antisecretory agents is used safely in this case?
CorrectC. Nizatidine. Similar to Ranitidine but principally metabolized in the kidney and bioavailability is 100%. Famotidine is similar to ranitidine but more potent. Cimetidine low dose given to patient with hepatic or renal failure. Ranitidine is longer acting and more potent than Cimetidine.
IncorrectC. Nizatidine. Similar to Ranitidine but principally metabolized in the kidney and bioavailability is 100%. Famotidine is similar to ranitidine but more potent. Cimetidine low dose given to patient with hepatic or renal failure. Ranitidine is longer acting and more potent than Cimetidine.
-
Question 88 of 175
88. Question
The short ciliary arteries and nerves are located in
CorrectE. SPCA and SPCN are located in 4 quadrants of the peripheral retina. The LPCN are located at 3 and 9 o’clock positions in the peripheral retina
IncorrectE. SPCA and SPCN are located in 4 quadrants of the peripheral retina. The LPCN are located at 3 and 9 o’clock positions in the peripheral retina
-
Question 89 of 175
89. Question
A patient walks into your office and performs a bruckner test. Upon illumination you notice the right eye has a dark/dull reflex and the left eye has a bright beautiful reflex. Which eye is the fixating eye and which is deviating?
CorrectA. OD and OS. Fixating the eye will absorb all light on the macula. Deviating eye will glow because light is focused on the non macula area.
IncorrectA. OD and OS. Fixating the eye will absorb all light on the macula. Deviating eye will glow because light is focused on the non macula area.
-
Question 90 of 175
90. Question
What test is MOST beneficial in determining stages of cancer in a patient?
CorrectC. Positron Emission Tomography is a scan that is used to analyze the metabolic activity of tissue. Because of this, PET scans are more helpful in determining the stage of cancer in an organ.
IncorrectC. Positron Emission Tomography is a scan that is used to analyze the metabolic activity of tissue. Because of this, PET scans are more helpful in determining the stage of cancer in an organ.
-
Question 91 of 175
91. Question
Which of the following is commonly employed for the treatment of ulcerative colitis?
CorrectA. Adalimumab – neutralization of TNF-alpha bioactivity by preventing the interaction of TNF-alpha with the cell surface TNF receptors
IncorrectA. Adalimumab – neutralization of TNF-alpha bioactivity by preventing the interaction of TNF-alpha with the cell surface TNF receptors
-
Question 92 of 175
92. Question
Using a Galilean telescope of +2.00D objective and -80D ocular lens, what is the tube length required to make this telescope function? What is the magnification?
CorrectD. 48.75 cm +40X
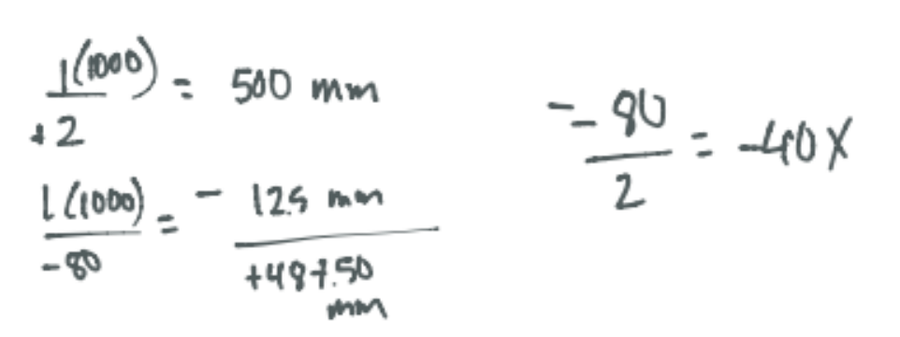 Incorrect
IncorrectD. 48.75 cm +40X

-
Question 93 of 175
93. Question
Which nucleus forms the tectotegmental tract?
CorrectB.The Edinger Westphal nucleus contains fibers that form the tectotegmental tract. The pretectal nucleus is not part of this tract. Pay close attention to the wording of this question. The tectotegmental tract is defined as the pretectal fibers projecting to both ipsilateral and contralateral edinger-westphal nuclei.
IncorrectB.The Edinger Westphal nucleus contains fibers that form the tectotegmental tract. The pretectal nucleus is not part of this tract. Pay close attention to the wording of this question. The tectotegmental tract is defined as the pretectal fibers projecting to both ipsilateral and contralateral edinger-westphal nuclei.
-
Question 94 of 175
94. Question
Maria is a 24 year old hispanic female suffering from chronic migraines. Which of the following beta blockers can you administer prophylactically to relieve her symptoms?
CorrectC. Propranolol. Is used to directly treat heart issues. Timolol is an ocular beta blocker used to treat glaucoma.
IncorrectC. Propranolol. Is used to directly treat heart issues. Timolol is an ocular beta blocker used to treat glaucoma.
-
Question 95 of 175
95. Question
Your patient presents with the following: AV nicking, Flame hemorrhages and cotton wool spots. According to Keith Wagener Barker’s hypertensive retinopathy classification, your patient can be classified as to be in stage___.
CorrectC. III. Grade 1: Mild, generalized constriction of retinal arterioles. Grade 2: Definite focal narrowing of retinal arterioles + AV nicking. Grade 3: Grade 2 + flame-shaped hemorrhages + cotton-wool spots + hard exudates. Grade 4: Severe Grade 3 retinopathy + papilledema or retinal edema.
IncorrectC. III. Grade 1: Mild, generalized constriction of retinal arterioles. Grade 2: Definite focal narrowing of retinal arterioles + AV nicking. Grade 3: Grade 2 + flame-shaped hemorrhages + cotton-wool spots + hard exudates. Grade 4: Severe Grade 3 retinopathy + papilledema or retinal edema.
-
Question 96 of 175
96. Question
Pfizer has just developed a new drug that they claim will cure prostate cancer. They are currently seeking 80-100 volunteers for a clinical trial where they will determine the optimal drug concentration to receive results. Which stage of clinical investigation are they currently undergoing?
CorrectA. 1. phase 2 looking for dose-response curve; phase 1 to determine toxicity and phase 3 prove efficacy
IncorrectA. 1. phase 2 looking for dose-response curve; phase 1 to determine toxicity and phase 3 prove efficacy
-
Question 97 of 175
97. Question
Which of the following is NOT a common side effect of cholinergic agonists?
CorrectA. Tachycardia is an adrenergic agonists response or cholinergic antagonistic response due. Cholinergic agonists promote parasympathetic responses. Think you use your cholen to relax and go to the bathroom. I.E. miosis, SLUDGE, bradycardia, vasodilation, bronchoconstriction.
IncorrectA. Tachycardia is an adrenergic agonists response or cholinergic antagonistic response due. Cholinergic agonists promote parasympathetic responses. Think you use your cholen to relax and go to the bathroom. I.E. miosis, SLUDGE, bradycardia, vasodilation, bronchoconstriction.
-
Question 98 of 175
98. Question
Five different patients: Vincent, Maria, Charlie, Delia and Malcolm are being treated with different lasers for a choroidal disease. Vincent is being treated with diode 850nm Charlie with argon 514nm, Maria with krypton 647nm, Delia with krypton 568nm and Malcom with dye 760nm. Based on the absorption transmission characteristic, which of the patients will receive the most effective treatment?
CorrectA. Want to treat choroidal layer so need to get past retinal layer. Higher wavelength will penetrate further.
IncorrectA. Want to treat choroidal layer so need to get past retinal layer. Higher wavelength will penetrate further.
-
Question 99 of 175
99. Question
A patient presents with symptoms mimicking retinitis pigmentosa. An ERG test was conducted and confirmed the suspected diagnosis. Which layer of the retina did the ERG test?
CorrectC. The outer retinal layers contain the photoreceptors to bipolar cells located in the inner nuclear layer, but does not include the ganglion cell layer.
IncorrectC. The outer retinal layers contain the photoreceptors to bipolar cells located in the inner nuclear layer, but does not include the ganglion cell layer.
-
Question 100 of 175
100. Question
Which materials are NOT considered hypoallergenic?
CorrectF. Polyamide
IncorrectF. Polyamide
-
Question 101 of 175
101. Question
The human red blood cells possess specific antigens which serve for identification. If after a motor vehicle accident a subject with blood group O requires transfusion of multiple blood units. The best product will be the one from a donor with blood group type?
CorrectC. Type O can only receive type O. AB is considered the universal recipient.
IncorrectC. Type O can only receive type O. AB is considered the universal recipient.
-
Question 102 of 175
102. Question
A Prescription for an aphakic patient reads:
OD: +16.00 DS
OS: +16.00 DS
Refracting distance of 14 mm.
This patient’s far point is located approximatelyCorrectC. vertex the power of the eye. This will help you find the patients far point F=16.00, L={16/(1-(0.014)(16)} = 48.5 mm behind the corneal apex.
IncorrectC. vertex the power of the eye. This will help you find the patients far point F=16.00, L={16/(1-(0.014)(16)} = 48.5 mm behind the corneal apex.
-
Question 103 of 175
103. Question
Angiotensin II will specifically promote which of the following?
CorrectB. Angiotensin II is a biochemical in the body that promotes expansion of the plasma volume by promoting the release of renal sodium and water absorption. This will cause vasodilation of the body blood vessels.
IncorrectB. Angiotensin II is a biochemical in the body that promotes expansion of the plasma volume by promoting the release of renal sodium and water absorption. This will cause vasodilation of the body blood vessels.
-
Question 104 of 175
104. Question
Which of the following laws states that each SCC influences a yoked pair of extraocular muscles?
CorrectB. Sherrington law : when one set of muscles is stimulated, muscles opposing the action of the first are simultaneously inhibited.
IncorrectB. Sherrington law : when one set of muscles is stimulated, muscles opposing the action of the first are simultaneously inhibited.
-
Question 105 of 175
105. Question
A patient was administered medication to treat an ocular bacterial infection. Not long after, he developed Steven Johnson Syndrome. What drug is known to cause this side effect?
CorrectB. Sulfacetamide. Sulfa drugs are directly linked to SJS symptoms or exacerbating SJS. Because of this they should be avoided at all times in patients even suspected of SJS.
IncorrectB. Sulfacetamide. Sulfa drugs are directly linked to SJS symptoms or exacerbating SJS. Because of this they should be avoided at all times in patients even suspected of SJS.
-
Question 106 of 175
106. Question
What is the refracting power of a 3X simple magnifier?
CorrectC. 12 D ; 3X=F/4 ; F=12D
IncorrectC. 12 D ; 3X=F/4 ; F=12D
-
Question 107 of 175
107. Question
What is it called when there are more electrons found in higher energy levels than the lower ground energy levels?
CorrectC. population inversion
IncorrectC. population inversion
-
Question 108 of 175
108. Question
Which cranial nerve is responsible for innervation of the main upper eyelid retractor?
CorrectB. CN3. Levator muscle is innervated by CN3. Muscle of mullers is a sympathetic innervation
IncorrectB. CN3. Levator muscle is innervated by CN3. Muscle of mullers is a sympathetic innervation
-
Question 109 of 175
109. Question
Which of the following wavelengths does the cornea absorb the most?
CorrectA. 100-280. This is known as the UV-C spectrum area. Cornea absorbs the UV-C and some UV-B. UV-B is mostly absorbed by the aqueous and the lens of the eye.
IncorrectA. 100-280. This is known as the UV-C spectrum area. Cornea absorbs the UV-C and some UV-B. UV-B is mostly absorbed by the aqueous and the lens of the eye.
-
Question 110 of 175
110. Question
A roommate of a college student is being treated in the hospital for acute meningococcal meningitis. It is wise to administer him prophylactic treatment with which of the following drugs?
CorrectC. Rifampin is a common medicine used to treat LTBI. It kills the sleeping TB germs before they make you sick.
IncorrectC. Rifampin is a common medicine used to treat LTBI. It kills the sleeping TB germs before they make you sick.
-
Question 111 of 175
111. Question
Four different lasers are used to treat using the photothermal type of mechanism. Laser JJJ uses a pulse exposure duration of 4 sec and a spot size of 45 microns. Laser AAA uses a pulse exposure duration of 8 sec. and a spot size of 35 micron. Laser ccc uses a pulse exposure duration of 8 sec. and spot size of 35 micron. Which one will give the LEAST damage
CorrectB. Laser JJJ Short time and bigger size will cause the least amount of damage
IncorrectB. Laser JJJ Short time and bigger size will cause the least amount of damage
-
Question 112 of 175
112. Question
A patient has read at six meters a standard Snellen letter labeled 20/40. Calculate the MAR.
CorrectB. 40/20= 2MAR
IncorrectB. 40/20= 2MAR
-
Question 113 of 175
113. Question
All of the following would differentiate between Megalocornea and Buphthalmos EXCEPT:
CorrectC. Megalocornea is determined by corneal diameter of greater than 10mm, abnormal axial length, and can lead to congenital glaucoma.
IncorrectC. Megalocornea is determined by corneal diameter of greater than 10mm, abnormal axial length, and can lead to congenital glaucoma.
-
Question 114 of 175
114. Question
What type of collagen is the sclera primarily composed of?
CorrectA. Type 1. Human scleral tissue contains approximately 50% collagen by weight, consisting predominantly of type I collagen. There is little or no evidence for the presence of substantial quantities of type II, type III or other collagen types.
IncorrectA. Type 1. Human scleral tissue contains approximately 50% collagen by weight, consisting predominantly of type I collagen. There is little or no evidence for the presence of substantial quantities of type II, type III or other collagen types.
-
Question 115 of 175
115. Question
Pantoscopic tilt of a spherical plus (+) lens induces a cyl. axis in which meridian? Face Form tilt of a spherical plus (+) lens induces a cyl. axis in which meridian? By cyl. axis we mean the axis of the spherocylinder in minus cyl. Notation.
CorrectA. 090:180. Plus lens induces plus cylinder on the axis. Panto induces on 180, faceform on 090. Since the answer has to be in minus cylinder form minus lens is induced on 090 for panto and faceform on 180.
IncorrectA. 090:180. Plus lens induces plus cylinder on the axis. Panto induces on 180, faceform on 090. Since the answer has to be in minus cylinder form minus lens is induced on 090 for panto and faceform on 180.
-
Question 116 of 175
116. Question
A 25 years old optometric student has his lung function evaluated through a spirometric exam. The following information is obtained from this exam: Total lung capacity: 6,000 ml., Vital capacity: 4,800 ml., Tidal volume: 500 ml; Residual volume; 1,200 ml. Knowing that his respiratory rate is 14 / minute please determine his minute ventilation.
CorrectD. 7000 ml. 500 x 14=7000 .Minute ventilation = tidal volume x respiratory rate
IncorrectD. 7000 ml. 500 x 14=7000 .Minute ventilation = tidal volume x respiratory rate
-
Question 117 of 175
117. Question
Which complication is MOST LIKELY expected after a YAG capsulotomy procedure?
CorrectA. Pupillary capture. YAG capsulotomy is the procedure of removing the capsular bag that is posterior to the IOL. Pupillary capture is an unusual complication of posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation and may occur in the early or late postoperative period
IncorrectA. Pupillary capture. YAG capsulotomy is the procedure of removing the capsular bag that is posterior to the IOL. Pupillary capture is an unusual complication of posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation and may occur in the early or late postoperative period
-
Question 118 of 175
118. Question
If peptic ulcer disease is diagnosed in a pregnant woman, then which of the following antisecretory agent must be avoided?
CorrectD. Misoprostol. Prostaglandin produces uterine contraction not used during pregnancy. Omeprazole Inhibits H+/K+ ATPase proton pump. Nizatidine H2 receptor antagonist. Cimetidine H2 receptor antagonist
IncorrectD. Misoprostol. Prostaglandin produces uterine contraction not used during pregnancy. Omeprazole Inhibits H+/K+ ATPase proton pump. Nizatidine H2 receptor antagonist. Cimetidine H2 receptor antagonist
-
Question 119 of 175
119. Question
Under steady fixation, the fading of stimuli with prolonged viewing is known as
CorrectB. troxler effect. Low temporal frequency stimuli is most noticeable in the peripheral vision
IncorrectB. troxler effect. Low temporal frequency stimuli is most noticeable in the peripheral vision
-
Question 120 of 175
120. Question
Pseudomembranous colitis is a complication known to occur with the use of?
CorrectA. Clindamycin works primarily by binding to the 50s ribosomal subunit of bacteria. This agent disrupts protein synthesis by interfering with the transpeptidation reaction, which thereby inhibits early chain elongation.
IncorrectA. Clindamycin works primarily by binding to the 50s ribosomal subunit of bacteria. This agent disrupts protein synthesis by interfering with the transpeptidation reaction, which thereby inhibits early chain elongation.
-
Question 121 of 175
121. Question
The left lung is unique in which of the following aspects?
CorrectC. Lacks a middle lobe. The left lung only has 2 lobes in order to allow the heart to fit. Right lung has 3 lobes.
IncorrectC. Lacks a middle lobe. The left lung only has 2 lobes in order to allow the heart to fit. Right lung has 3 lobes.
-
Question 122 of 175
122. Question
Of the Anti-Leukotriene drugs, all are effective orally and all but one inhibit cytochrome P450. Which of the following does NOT inhibit Cytochrome P450?
CorrectA. Theophylline is used to prevent and treat wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness caused by asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and other lung disease. It is the only one that inhibits Cytochrome P450
IncorrectA. Theophylline is used to prevent and treat wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness caused by asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and other lung disease. It is the only one that inhibits Cytochrome P450
-
Question 123 of 175
123. Question
Which of the following is more relevant to chrysiasis?
CorrectA. Rheumatoid arthritis. Chrysiasis is the phenomenon of bluish to slate-gray skin pigmentation induced by prolonged treatment with gold salts. The most common etiology is the administration of gold salts to patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
IncorrectA. Rheumatoid arthritis. Chrysiasis is the phenomenon of bluish to slate-gray skin pigmentation induced by prolonged treatment with gold salts. The most common etiology is the administration of gold salts to patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Question 124 of 175
124. Question
According to Kollner’s rule which color vision anomaly is expected in a patient with age related macular degeneration?
CorrectB. Blue- yellow affect macular region. Red green affects ONH
IncorrectB. Blue- yellow affect macular region. Red green affects ONH
-
Question 125 of 175
125. Question
Which of the following have low survivability outcomes for patients?
CorrectA. Non- hodgkins lymphoma has a poorer outcome in patients than the other options listed. All prognosis are good if caught early, however the most aggressive cancer of the ones listed is non-hodgkin’s lymphoma.
IncorrectA. Non- hodgkins lymphoma has a poorer outcome in patients than the other options listed. All prognosis are good if caught early, however the most aggressive cancer of the ones listed is non-hodgkin’s lymphoma.
-
Question 126 of 175
126. Question
Which of the following structures of the eye would MOST be affected by thermal damage after a very short exposure to UV light?
CorrectB. Cornea is the main protector of the eye from UV light. Particularly UV-C and some UV-B. The lens absorbs UV-B and UV-A. The retina does not absorb any UV light.
IncorrectB. Cornea is the main protector of the eye from UV light. Particularly UV-C and some UV-B. The lens absorbs UV-B and UV-A. The retina does not absorb any UV light.
-
Question 127 of 175
127. Question
On a lensometer, what is the main device that detects parallel light?
CorrectD. Telescope.
IncorrectD. Telescope.
-
Question 128 of 175
128. Question
Angle between pupillary axis and nodal axis is referred to as?
CorrectA. Angle Kappa. Angle lambda is the angle between pupillary axis and line of sight. Angle alpha is the angle between optic axis and visual axis. Angle gamma is the angle between fixation axis and the optical axis.
IncorrectA. Angle Kappa. Angle lambda is the angle between pupillary axis and line of sight. Angle alpha is the angle between optic axis and visual axis. Angle gamma is the angle between fixation axis and the optical axis.
-
Question 129 of 175
129. Question
Which of the following adrenoreceptors mediates increased tachycardia and increased lipolysis?
CorrectA. B1 is found on the heart. B2 found on the lungs
IncorrectA. B1 is found on the heart. B2 found on the lungs
-
Question 130 of 175
130. Question
What type of agent would be at B?
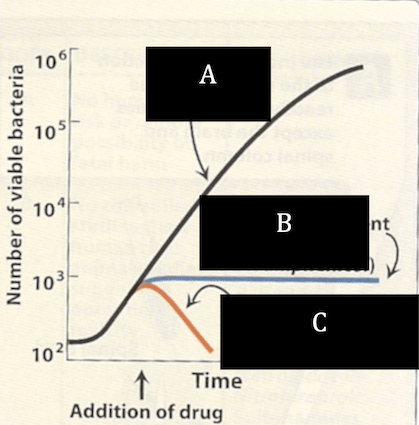 Correct
CorrectB. Bacteriostatic. The number of bacteria does not grow as more of the drug is administered. C. is bactericidal since the number of bacteria decreases as the amount of drug and increase of time with the drug occurs.
IncorrectB. Bacteriostatic. The number of bacteria does not grow as more of the drug is administered. C. is bactericidal since the number of bacteria decreases as the amount of drug and increase of time with the drug occurs.
-
Question 131 of 175
131. Question
Oxygenated blood is carried into the heart through which of the following blood vessels of the lung?
CorrectC. Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood to the heart. Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood to the heart.
IncorrectC. Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood to the heart. Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood to the heart.
-
Question 132 of 175
132. Question
If a keratometer is calibrated for a corneal index of 1.3376, with 76mm diameter mire, 3mm diameter of the image, what is the K reading if the mire is located 76.66 mm aways from the cornea?
CorrectD. +55.75D
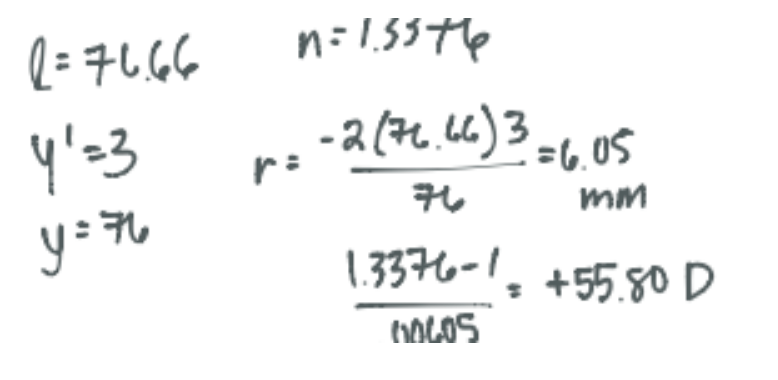 Incorrect
IncorrectD. +55.75D
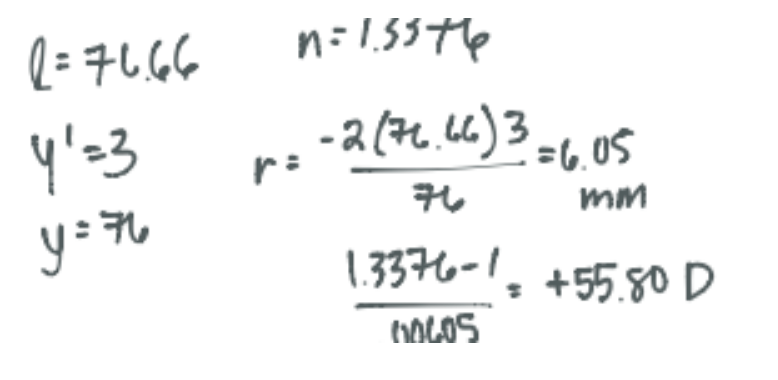
-
Question 133 of 175
133. Question
A 85 year old grandmother attends the doctor’s office. She complains she has short-term memory loss, and she seems to have no idea why her child brought her to this “horribly bright and white room with this stranger”. You diagnose the grandmother with Alzheimer’s disease. What drug should be prescribed to increase the amount of Ach in her brain to help treat it?
CorrectThe correct answer is:
D. Donepezil
Donepezil is a centrally acting acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It increases the concentration of acetylcholine (Ach) in the brain by slowing its breakdown, which can help improve symptoms in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
Here’s why the other options are not appropriate:
-
Physostigmine: Can cross the blood-brain barrier but is not used long-term for Alzheimer’s. It’s mainly used for anticholinergic toxicity.
-
Neostigmine: Does not cross the blood-brain barrier. It’s used for peripheral conditions like myasthenia gravis.
-
Echothiophate: An irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, mainly used in ophthalmology. Too toxic for systemic or chronic use in Alzheimer’s.
So, Donepezil is the best choice here.
IncorrectThe correct answer is:
D. Donepezil
Donepezil is a centrally acting acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It increases the concentration of acetylcholine (Ach) in the brain by slowing its breakdown, which can help improve symptoms in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
Here’s why the other options are not appropriate:
-
Physostigmine: Can cross the blood-brain barrier but is not used long-term for Alzheimer’s. It’s mainly used for anticholinergic toxicity.
-
Neostigmine: Does not cross the blood-brain barrier. It’s used for peripheral conditions like myasthenia gravis.
-
Echothiophate: An irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, mainly used in ophthalmology. Too toxic for systemic or chronic use in Alzheimer’s.
So, Donepezil is the best choice here.
-
Question 134 of 175
134. Question
A father with anomalous color vision marries a mother that is a carrier. What percent of all their children will have anomalous color vision?
CorrectC. 50 percent.
IncorrectC. 50 percent.
-
Question 135 of 175
135. Question
What vitreous if formed in the posterior chamber?
CorrectC. tertiary. Tertiary forms zonules that are located in the posterior chamber. Primary vitreous is dissolved upon development of the orbital.
IncorrectC. tertiary. Tertiary forms zonules that are located in the posterior chamber. Primary vitreous is dissolved upon development of the orbital.
-
Question 136 of 175
136. Question
You are working in the ER late one night, and a patient comes in who is having a severe heart attack with left ventricular failure. You know that this type of heart problem can cause pulmonary edema and as a result, high blood pressure. What drug should you give in this situation to reduce the BP?
CorrectA. Trimethaphan counteracts cholinergic transmission at the ganglion type of nicotinic receptors of the autonomic ganglia and therefore blocks both the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system
IncorrectA. Trimethaphan counteracts cholinergic transmission at the ganglion type of nicotinic receptors of the autonomic ganglia and therefore blocks both the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system
-
Question 137 of 175
137. Question
What part of latanoprostene bundo works exclusively on the trabecular meshwork?
CorrectB. Latanoprostene bundo is a combination drug that works on both the trabecular meshwork and the uveal scleral outflow. It is made up of prostaglandin and nitric oxide. Prostaglandin works on the uveal scleral outflow and nitric oxide works on the Trabecular meshwork.
IncorrectB. Latanoprostene bundo is a combination drug that works on both the trabecular meshwork and the uveal scleral outflow. It is made up of prostaglandin and nitric oxide. Prostaglandin works on the uveal scleral outflow and nitric oxide works on the Trabecular meshwork.
-
Question 138 of 175
138. Question
Which of the following radiations would cause the MOST internal non-ionizing damage to the eye structures?
CorrectE. Of the non ionizing, UV-B causes the most damage (low wavelength)
IncorrectE. Of the non ionizing, UV-B causes the most damage (low wavelength)
-
Question 139 of 175
139. Question
Which retinal cells are formed by cells of the outer neuroblastic layer?
CorrectC. Bipolar cells. The inner neuroblastic layer forms amacrine, ganglion, and muller cells. The outer neuroblastic layer formes photoreceptor, bipolar, and horizontal
IncorrectC. Bipolar cells. The inner neuroblastic layer forms amacrine, ganglion, and muller cells. The outer neuroblastic layer formes photoreceptor, bipolar, and horizontal
-
Question 140 of 175
140. Question
Which purkinje image is used when measuring the cornea on a keratometer?
CorrectA. I. Purkinje image 1 is focused on the anterior aspect of the cornea. II is the posterior aspect of the cornea. III is the anterior aspect of the lens. IV is the posterior aspect of the lens as well as the only image that is inverted and real
IncorrectA. I. Purkinje image 1 is focused on the anterior aspect of the cornea. II is the posterior aspect of the cornea. III is the anterior aspect of the lens. IV is the posterior aspect of the lens as well as the only image that is inverted and real
-
Question 141 of 175
141. Question
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor associated with long term use of omeprazole?
CorrectA. Secondary hypogastrinemia. Omeprazole caused hypergastrinemia
IncorrectA. Secondary hypogastrinemia. Omeprazole caused hypergastrinemia
-
Question 142 of 175
142. Question
If a patient has paralysis of cranial nerve IV, then which of the following is the most likely outcome?
CorrectA. Intorsion of the eye. CN4 innervates the SO. The SO primary function is intorsion
IncorrectA. Intorsion of the eye. CN4 innervates the SO. The SO primary function is intorsion
-
Question 143 of 175
143. Question
If a person with high minus spectacle prescription switches to contact lens, the power on the contact lens would be which of the following when compared to the power of the spectacle lens?
CorrectA. less than. As you move a minus les closer to the eye, the effective power increases; this mean it gains more plus power. We compensate for this effective power by prescribing less power as we get closer to the eye which is why contact lenses are more plus compared to the glasses prescription.
IncorrectA. less than. As you move a minus les closer to the eye, the effective power increases; this mean it gains more plus power. We compensate for this effective power by prescribing less power as we get closer to the eye which is why contact lenses are more plus compared to the glasses prescription.
-
Question 144 of 175
144. Question
Which of the following antiviral agents of choice is used to treat herpes simplex virus keratoconjunctivitis?
CorrectD. Trifluridine (Viroptic) is a fluorinated pyrimidine nucleoside which irreversibly inhibits thymidylate synthase and specific DNA polymerases, necessary for the conversion of dUMP to dTMP in the process of DNA synthesis
IncorrectD. Trifluridine (Viroptic) is a fluorinated pyrimidine nucleoside which irreversibly inhibits thymidylate synthase and specific DNA polymerases, necessary for the conversion of dUMP to dTMP in the process of DNA synthesis
-
Question 145 of 175
145. Question
A patient is able to read the 20/20 line at 7 cm. What is the size of that letter that the patient is able to read?
CorrectA. 10.18mm ; (0.07/6)(8.73)(20/20)= 10.18mm
IncorrectA. 10.18mm ; (0.07/6)(8.73)(20/20)= 10.18mm
-
Question 146 of 175
146. Question
Which of the following diseases are directly caused by a ABCA4 mutation?
CorrectA. Stargardt’s disease is directly caused by a mutation in the ABCA4 membrane protein and is responsible for moving all trans retinal from the photoreceptor to the cytoplasm
IncorrectA. Stargardt’s disease is directly caused by a mutation in the ABCA4 membrane protein and is responsible for moving all trans retinal from the photoreceptor to the cytoplasm
-
Question 147 of 175
147. Question
Decreasing diameter:
CorrectB. can lessen edema. When we decrease diameter there is less surface area covering the cornea as well as having a flatter contact lens. This can increase the movement of the lens
IncorrectB. can lessen edema. When we decrease diameter there is less surface area covering the cornea as well as having a flatter contact lens. This can increase the movement of the lens
-
Question 148 of 175
148. Question
Which receptive fields of the LGN respond to blue-yellow contrast?
CorrectC. Konio cells. Magno cells are sensitive to fast movements and large details. Parvo cells are sensitive to red green and fine details.
IncorrectC. Konio cells. Magno cells are sensitive to fast movements and large details. Parvo cells are sensitive to red green and fine details.
-
Question 149 of 175
149. Question
A lens clock measures: Front surface @090 =+8.00D. Front surfaces @180 =+7.00 D. Ocular surface = -5.00D. What would the approximate power of the lens be if the lens were made from plastic n=1.60?
CorrectD.
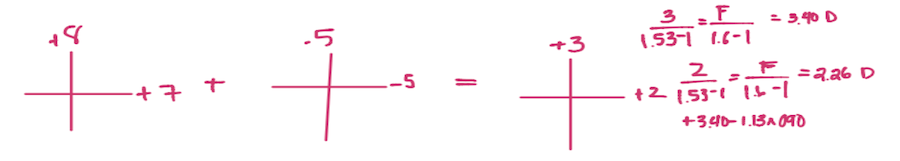 Incorrect
IncorrectD.
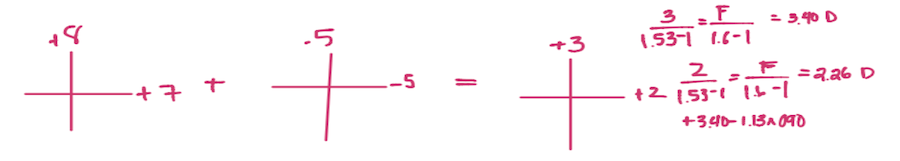
-
Question 150 of 175
150. Question
A patient comes to your office with a spectacle prescription of -8.50-1.00×180. His chief complaint is blurry vision at distance with his spectacles and notices an improvement with what you observe is a pantoscopic tilt of the spectacles. What change in his refractive error would you expect according to his chief complaint?
CorrectE. Increase myopia and with the rule astigmatism. Remember panto tilt increases the power of the 180 axis
IncorrectE. Increase myopia and with the rule astigmatism. Remember panto tilt increases the power of the 180 axis
-
Question 151 of 175
151. Question
Damage of which of the following cranial nerves leads to anosmia?
CorrectB. CN2 innervates smell. Anosmia is the loss of smell
IncorrectB. CN2 innervates smell. Anosmia is the loss of smell
-
Question 152 of 175
152. Question
What is the refractive power of the human cornea 1 week after birth?
CorrectC. 48 diopters. At birth a baby has 48 diopters of power. This is lost at a rate of 2 diopters per year until the age of 2.
IncorrectC. 48 diopters. At birth a baby has 48 diopters of power. This is lost at a rate of 2 diopters per year until the age of 2.
-
Question 153 of 175
153. Question
An aphakic patient was refracted at 14 mm and found +16.50 D. If the spectacles are going to be worn with a vertex of 8mm; what back vertex power must the lenses have?
CorrectE. +18.37 DS.
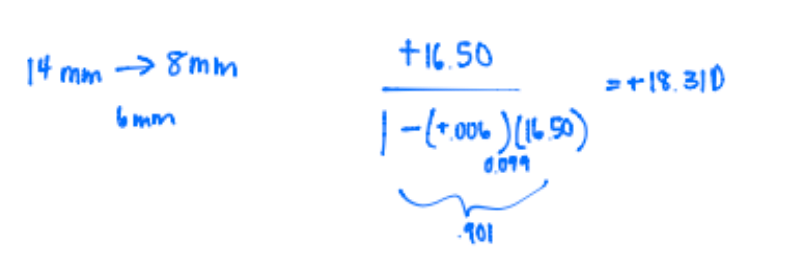 Incorrect
IncorrectE. +18.37 DS.
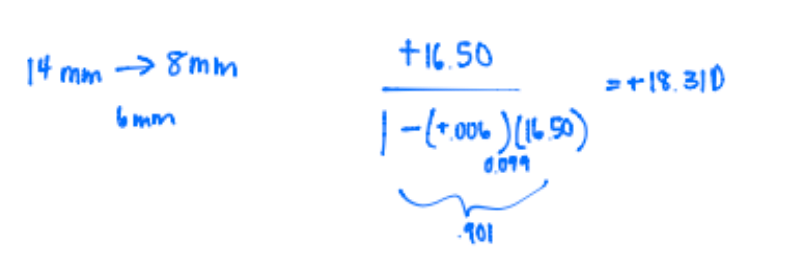
-
Question 154 of 175
154. Question
Which of the following signs specifically supports the diagnosis of congenital ptosis?
CorrectC. absent or minimal lid crease is the main factor in determining if a ptosis is congenital or mechanical. During the development phase of the human eye all muscles and tendons must develop properly to show a lid crease. If there is a malformation then the lid crease is not going to show.
IncorrectC. absent or minimal lid crease is the main factor in determining if a ptosis is congenital or mechanical. During the development phase of the human eye all muscles and tendons must develop properly to show a lid crease. If there is a malformation then the lid crease is not going to show.
-
Question 155 of 175
155. Question
What is the partial pressure of oxygen within the tears?
CorrectC. 155mm HG under open eye conditions will oxygen partial pressure be a factor
IncorrectC. 155mm HG under open eye conditions will oxygen partial pressure be a factor
-
Question 156 of 175
156. Question
Starch and cellulose are classified as what type of carbohydrate?
CorrectC. Homopolysaccharide. They are made up of repeating sugar units that do not differentiate on the side chain. Heteropolysaccharides are hyaluronic acid which is found in areas of high impact. These polysaccharides are aligned in a lattice style structure causing an increase in surface area for flexion.
IncorrectC. Homopolysaccharide. They are made up of repeating sugar units that do not differentiate on the side chain. Heteropolysaccharides are hyaluronic acid which is found in areas of high impact. These polysaccharides are aligned in a lattice style structure causing an increase in surface area for flexion.
-
Question 157 of 175
157. Question
Old red blood cells usually are removed from the peripheral circulation after approximately __ days after maturation.
CorrectC. 120 days.
IncorrectC. 120 days.
-
Question 158 of 175
158. Question
When a lensometer reads plano, the target should be where:
CorrectA. Primary focal length coincides with the far point of a lens. If the far point of a lens is at infinity then the power of the lens is plano.
IncorrectA. Primary focal length coincides with the far point of a lens. If the far point of a lens is at infinity then the power of the lens is plano.
-
Question 159 of 175
159. Question
A doctor has reduced the size of a chart to work at 10 feet. The patient needs to be brought to 8 feet to see the 20/400 line. What is the VA of the patient?
CorrectD. 20/500 ; (10/8)(400)=500
IncorrectD. 20/500 ; (10/8)(400)=500
-
Question 160 of 175
160. Question
Barrel distortion is produced by an ophthalmic lens with overall ___ power?
CorrectB. Minus.
Minus lens makes barrel distortion. Plus lens makes pincushion distortion.IncorrectB. Minus.
Minus lens makes barrel distortion. Plus lens makes pincushion distortion. -
Question 161 of 175
161. Question
Which of the following are adverse effects of pyogenesis? (SELECT 3)
CorrectA,B,E. Pyogenesis is defined as the production of heat. Dehydration is a main adverse effect of heat conduction due to the increased lacrimation of the sweat glands. Fever is self explanatory. If the body produces too much heat it can lead to severe brain damage and thus shut off major motor functions in the body
IncorrectA,B,E. Pyogenesis is defined as the production of heat. Dehydration is a main adverse effect of heat conduction due to the increased lacrimation of the sweat glands. Fever is self explanatory. If the body produces too much heat it can lead to severe brain damage and thus shut off major motor functions in the body
-
Question 162 of 175
162. Question
The medial portion of the eyelid lymphatics drain into which of the following structures?
CorrectD. Submandibular lymph node. lateral 2/3 of the upper lid and the lateral 1/3 of the lower lid lymphatics drain into the preauricular lymph node. The medial 1/3 of the upper eyelid and the medial 2/3 of the lower lid lymphatics drain into the submandibular node.
IncorrectD. Submandibular lymph node. lateral 2/3 of the upper lid and the lateral 1/3 of the lower lid lymphatics drain into the preauricular lymph node. The medial 1/3 of the upper eyelid and the medial 2/3 of the lower lid lymphatics drain into the submandibular node.
-
Question 163 of 175
163. Question
A 34 year old female with a history of trauma to the head comes in seeing double vision OU with light sensitivity in OD. You correctly diagnose the patient with iridodialysis. What part of the iris is affected?
CorrectC. Iris root is the thinnest portion of the iris. Because of this it is the most easily susceptible portion of the iris to be torn.
IncorrectC. Iris root is the thinnest portion of the iris. Because of this it is the most easily susceptible portion of the iris to be torn.
-
Question 164 of 175
164. Question
A monochromatic stimulus of _____ nm appears less saturated (whiter) than any other monochromatic stimulus
CorrectB. 555. Hue null point is set to 555 which will appear less saturated than any other point
IncorrectB. 555. Hue null point is set to 555 which will appear less saturated than any other point
-
Question 165 of 175
165. Question
Assume a laser radiation with wavelength of 685 nm. The laser is treating a fissure which consists of molecules with size of 0.001 mm. Which of the following should MOST likely occur?
CorrectD. The Mie theory is a complete mathematical–physical theory of the scattering of electromagnetic wave by homogeneous spherical particles, developed by Gustav Mie in 1908. In contrast to Rayleigh scattering, the Mie theory embraces all possible ratios of the particle radius to wavelength.
IncorrectD. The Mie theory is a complete mathematical–physical theory of the scattering of electromagnetic wave by homogeneous spherical particles, developed by Gustav Mie in 1908. In contrast to Rayleigh scattering, the Mie theory embraces all possible ratios of the particle radius to wavelength.
-
Question 166 of 175
166. Question
All of the following occurs during stimulated emission of light in lasers EXCEPT
CorrectA. Not possible. Cannot have two light wavelength at the same time.
IncorrectA. Not possible. Cannot have two light wavelength at the same time.
-
Question 167 of 175
167. Question
A patient is currently prescribed Travatan. Which of the following below is the best topical add-on to achieve a synergistic effect?
CorrectA. Dorzolamide. Travatan is a prostaglandin that acts on the uveoscleral outflow mechanism. Dorzolamide is a CAI that works on the production of aqueous humor. Imagine the eye as a sink that is turned out and the drain is clogged. Prostaglandin will clean out the drain but the water is still overflowing. The only other logical thing to do is to shut off the water or reduce the amount of water coming in. This same principal can be applied to the effect of travatan on the aqueous humor mechanism.
IncorrectA. Dorzolamide. Travatan is a prostaglandin that acts on the uveoscleral outflow mechanism. Dorzolamide is a CAI that works on the production of aqueous humor. Imagine the eye as a sink that is turned out and the drain is clogged. Prostaglandin will clean out the drain but the water is still overflowing. The only other logical thing to do is to shut off the water or reduce the amount of water coming in. This same principal can be applied to the effect of travatan on the aqueous humor mechanism.
-
Question 168 of 175
168. Question
Which mirror of a goldmann gonioscopic lens would you use to view the posterior ora serrata?
CorrectD. 67 degree mirror. The more angled the mirror the more anterior the structure you will see. Trapezoid or 73 degree mirror is used to see the equator of the eye.
IncorrectD. 67 degree mirror. The more angled the mirror the more anterior the structure you will see. Trapezoid or 73 degree mirror is used to see the equator of the eye.
-
Question 169 of 175
169. Question
Which of the following medications is best known to treat myokymia?
CorrectB. Zyrtec is a second generation antihistamine that has an off label treatment for eyelid myokymia. However there is no understanding to why this works.
IncorrectB. Zyrtec is a second generation antihistamine that has an off label treatment for eyelid myokymia. However there is no understanding to why this works.
-
Question 170 of 175
170. Question
Which of the following structures is responsible for maintaining intraocular pressure?
CorrectB. Ciliary muscle when stimulated will pull on the scleral spur thus opening the Uveal scleral outflow pathway
IncorrectB. Ciliary muscle when stimulated will pull on the scleral spur thus opening the Uveal scleral outflow pathway
-
Question 171 of 175
171. Question
Broca’s areas is supplied by which of the following?
CorrectB. middle cerebral artery. Broca’s area is located in the frontal gyrus of the left side of the brain. If damaged the patient can experience aphasia.
IncorrectB. middle cerebral artery. Broca’s area is located in the frontal gyrus of the left side of the brain. If damaged the patient can experience aphasia.
-
Question 172 of 175
172. Question
According to the OATS study which of the following treatment options was shown to reduce chances of glaucoma progression?
CorrectA. Topical ocular hypotensive medications such as latanoprost was affected in delay or prevent POAG individual with elevated IOP by 30% once IOP pressure was between 24 and 32 mm Hg
IncorrectA. Topical ocular hypotensive medications such as latanoprost was affected in delay or prevent POAG individual with elevated IOP by 30% once IOP pressure was between 24 and 32 mm Hg
-
Question 173 of 175
173. Question
Methotrexate affects which of the following systems? (SELECT 2)
CorrectA.F. Methotrexate. Methotrexate is in a class of medications called antimetabolites. Methotrexate treats cancer by slowing the growth of cancer cells. Methotrexate treats psoriasis by slowing the growth of skin cells to stop scales from forming. Methotrexate may treat rheumatoid arthritis by decreasing the activity of the immune system.
IncorrectA.F. Methotrexate. Methotrexate is in a class of medications called antimetabolites. Methotrexate treats cancer by slowing the growth of cancer cells. Methotrexate treats psoriasis by slowing the growth of skin cells to stop scales from forming. Methotrexate may treat rheumatoid arthritis by decreasing the activity of the immune system.
-
Question 174 of 175
174. Question
A patient requires a prescription of +6.00 D in contacts. What power is needed at a vertex distance of 14 mm?
CorrectD. +5.50 D
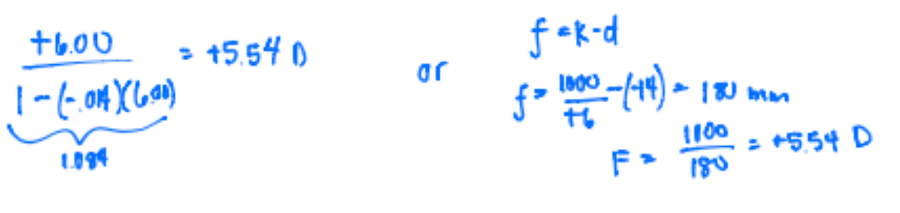 Incorrect
IncorrectD. +5.50 D
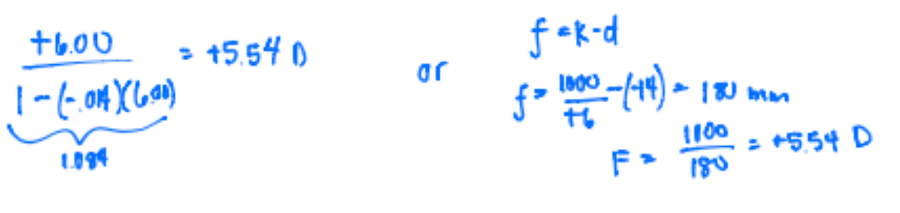
-
Question 175 of 175
175. Question
The blood retinal barrier includes
CorrectC. The ELM is composed of zonula adherens. The bruch membrane provides no barrier function but acts more like a shock absorber to the retina because of its elastic core
IncorrectC. The ELM is composed of zonula adherens. The bruch membrane provides no barrier function but acts more like a shock absorber to the retina because of its elastic core
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- Answered
- Review