NBEO® Part 1 Full Length Test #2 - Ophthalmic Optics
Next
0 of 29 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
Information
|
Optometry Board Practice Test for the NBEO® Part 1 Test #2 – Ophthalmic Optics This test is comprised of 29 items, which must be completed within 29 minutes. |
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Exam is loading ...
You must sign in or sign up to start the exam.
You have to finish following exam, to start this exam:
Results
0 of 29 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You answered 0 of 0 (0) questions correct
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Ophthalmic Optics 0%
- Ophthalmic Optics: Lasers 0%
-
Based on your performance on this Optometry Board Part 1 Practice Test, you’re not yet ready for the NBEO® Part 1.
Keep your head up! Also, don’t focus on your estimated score, they mean essentially nothing at the start. Rarely does anyone start these exams and score well immediately, if that was the case then they wouldn’t even need to practice! These are ‘practice’ tests, meaning you’re practicing to improve your skills. If you continue to work hard and study, read and understand the solutions, practice with “OptometryBoards.com” daily and give it your best effort, we promise your score will improve. Review and learn for now, and the scores will come.
-The “OptometryBoards.com” Team
-
Congratulations! Based on your performance on this Optometry Board Part 1 Practice Test, you’re predicted to pass your NBEO® Part 1! Keep hammering away at our Optometry Board questions so that you can keep up the great work!
-The “OptometryBoards.com” Team
-
Question 1 of 29
1. Question
Which materials are NOT considered hypoallergenic?
CorrectF. Polyamide
IncorrectF. Polyamide
-
Question 2 of 29
2. Question
A frame has the following dimensions: A= b/ mm B=48 mm C=50 mm DBC=-67 mm Seg drop= 7 mm. What is the segment height?
Correcta. 17mm. Seg height= 0.5(A)- seg drop
Incorrecta. 17mm. Seg height= 0.5(A)- seg drop
-
Question 3 of 29
3. Question
A certain lens of index of 1.67 has a convex spherical front surface. The sag of the front surface is 1.2 mm for a chord whose length is 20 mm. What is the power of the front surface?
CorrectD. R=(10^2)/2(1.2) + (1.2/2) =42.27mm
IncorrectD. R=(10^2)/2(1.2) + (1.2/2) =42.27mm
-
Question 4 of 29
4. Question
A lens has a power of pl -2.00×090 it is decentered 2 mm nasally and edged 50 mm round. Which edge is the thickest?
CorrectC. Temporal. Plus lenses are thicker in the center. Minus lenses are thicker in the periphery. Draw the lens in a lens cross with this key in mind.
IncorrectC. Temporal. Plus lenses are thicker in the center. Minus lenses are thicker in the periphery. Draw the lens in a lens cross with this key in mind.
-
Question 5 of 29
5. Question
Vertical imbalance must be corrected for reading level 10 mm below the distance OC for the following prescription:
OD: -1.00-2.00×180
OS: -1.00-3.00×180
Add: +2.00
Segment drop of 5mmWhich of the following segment drops would allow for a drop of 5 mm?
CorrectD. FT28 has a seg drop of 5mm. FT40 has a seg drop of 20. Round 22 has a seg drop of 11 mm Round 38 has a seg drop of 19 mm
IncorrectD. FT28 has a seg drop of 5mm. FT40 has a seg drop of 20. Round 22 has a seg drop of 11 mm Round 38 has a seg drop of 19 mm
-
Question 6 of 29
6. Question
Which of the following radiations would cause the MOST internal non-ionizing damage to the eye structures?
CorrectE. Of the non ionizing, UV-B causes the most damage (low wavelength)
IncorrectE. Of the non ionizing, UV-B causes the most damage (low wavelength)
-
Question 7 of 29
7. Question
Which of the following wavelengths of laser light is considered to be the MOST effective for the treatment of the macula but avoiding damage to the macula?
CorrectA. Further from blue, it is the safest (red)
IncorrectA. Further from blue, it is the safest (red)
-
Question 8 of 29
8. Question
Which laser used for eye surgical procedure is considered the safest under the FDA classification of lasers?
CorrectE. Only one that is a class one laser and is USED in surgical procedures. He-ne is also class one but is not USED in surgical procedures.
IncorrectE. Only one that is a class one laser and is USED in surgical procedures. He-ne is also class one but is not USED in surgical procedures.
-
Question 9 of 29
9. Question
Five different patients: Vincent, Maria, Charlie, Delia and Malcolm are being treated with different lasers for a choroidal disease. Vincent is being treated with diode 850nm Charlie with argon 514nm, Maria with krypton 647nm, Delia with krypton 568nm and Malcom with dye 760nm. Based on the absorption transmission characteristic, which of the patients will receive the most effective treatment?
CorrectA. Want to treat choroidal layer so need to get past retinal layer. Higher wavelength will penetrate further.
IncorrectA. Want to treat choroidal layer so need to get past retinal layer. Higher wavelength will penetrate further.
-
Question 10 of 29
10. Question
Which of the following structures of the eye would MOST be affected by thermal damage after a very short exposure to UV light?
CorrectB. Cornea is the main protector of the eye from UV light. Particularly UV-C and some UV-B. The lens absorbs UV-B and UV-A. The retina does not absorb any UV light.
IncorrectB. Cornea is the main protector of the eye from UV light. Particularly UV-C and some UV-B. The lens absorbs UV-B and UV-A. The retina does not absorb any UV light.
-
Question 11 of 29
11. Question
Five different lasers are being used laser “A” has a wavelength of 532 nm and uses a pulse of 10ms. Laser “B” has wavelength of 1064 nm and uses pulse of 10ns, Laser “C” has wavelength of 527 nm and pulse of 20ps, Laser “D” has wavelength of 1053nm and uses pulse of 20ps and Laser “E” has wavelength of 7450nm with pulse of 50ps. Which of the following lasers will most likely cause a photochemical damage mechanism?
CorrectC. Need low wavelength and fast pulse = strong power and fast pulse
IncorrectC. Need low wavelength and fast pulse = strong power and fast pulse
-
Question 12 of 29
12. Question
An argon laser emits light of power 16 watts in 2 sec. The beam area size is 0.5 square cm. Beam divergence is 2 mrad the beam diameter is 3 mm. What is the irradiance emitted by the laser?
CorrectC. 16/0.5 = 32
IncorrectC. 16/0.5 = 32
-
Question 13 of 29
13. Question
An argon laser emits light of power 16 watts in 2 sec. The beam area size is 0.5 square cm. Beam divergence is 2 mrad the beam diameter is 3 mm. what would the irradiance if the power emitted by the laser is 16 watts in 4 sec. assume that the beam divergence and the beam diameter are the same as above
CorrectB. Answer doesn’t change due to the equation. 16/0.5 = 32
IncorrectB. Answer doesn’t change due to the equation. 16/0.5 = 32
-
Question 14 of 29
14. Question
Assume a laser radiation with wavelength of 685 nm. The laser is treating a fissure which consists of molecules with size of 0.001 mm. Which of the following should MOST likely occur?
CorrectD. The Mie theory is a complete mathematical–physical theory of the scattering of electromagnetic wave by homogeneous spherical particles, developed by Gustav Mie in 1908. In contrast to Rayleigh scattering, the Mie theory embraces all possible ratios of the particle radius to wavelength.
IncorrectD. The Mie theory is a complete mathematical–physical theory of the scattering of electromagnetic wave by homogeneous spherical particles, developed by Gustav Mie in 1908. In contrast to Rayleigh scattering, the Mie theory embraces all possible ratios of the particle radius to wavelength.
-
Question 15 of 29
15. Question
All of the following occurs during stimulated emission of light in lasers EXCEPT
CorrectA. Not possible. Cannot have two light wavelength at the same time.
IncorrectA. Not possible. Cannot have two light wavelength at the same time.
-
Question 16 of 29
16. Question
Which of the following lasers is highly used to treat recurrent corneal erosions?
CorrectA. Nd Yag
IncorrectA. Nd Yag
-
Question 17 of 29
17. Question
Four different lasers are used to treat using the photothermal type of mechanism. Laser JJJ uses a pulse exposure duration of 4 sec and a spot size of 45 microns. Laser AAA uses a pulse exposure duration of 8 sec. and a spot size of 35 micron. Laser ccc uses a pulse exposure duration of 8 sec. and spot size of 35 micron. Which one will give the LEAST damage
CorrectB. Laser JJJ Short time and bigger size will cause the least amount of damage
IncorrectB. Laser JJJ Short time and bigger size will cause the least amount of damage
-
Question 18 of 29
18. Question
A lens clock reads as follows on its major meridians: 160 degree meridian front surface +4.00 D, back surface -6.00 D 70 degree meridian; front surface +4.00 D, back surface -8.00 D. Assuming the lens material has an index of 1.53, what is the approximate prescription (nominal) in PLUS cylinder form?
CorrectD.
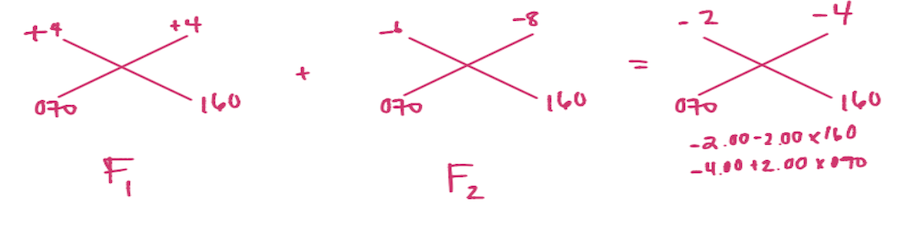 Incorrect
IncorrectD.
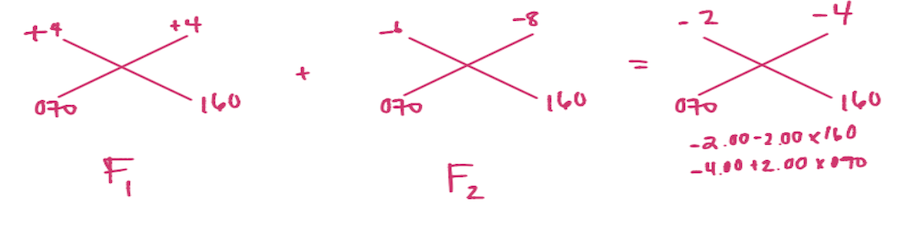
-
Question 19 of 29
19. Question
You hand neutralize a lens and find no motion when a -1.50D trial lens is used along the 90 degree meridian (moving lens up and down) and no motion when a -1.00 D trial lens is ADDED to the initial -1.50 D lens used along the 180 degree meridian (moving side to side). What is the power of the lens?
CorrectC.
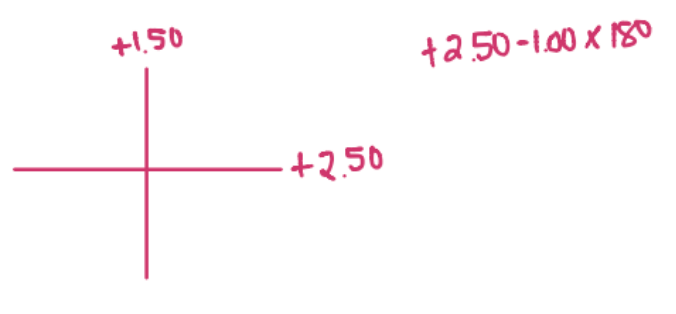 Incorrect
IncorrectC.
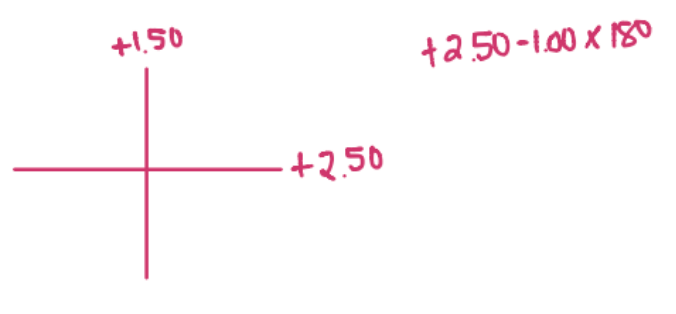
-
Question 20 of 29
20. Question
Which of the following lens materials has the least amount of dispersive power?
CorrectA. CR-39. The higher the abbe value the less amount of CA there is. CR 39 abbe 58, Polycarbonate abbe 30, Trivex abbe 43
IncorrectA. CR-39. The higher the abbe value the less amount of CA there is. CR 39 abbe 58, Polycarbonate abbe 30, Trivex abbe 43
-
Question 21 of 29
21. Question
Barrel distortion is produced by an ophthalmic lens with overall ___ power?
CorrectB. Minus.
Minus lens makes barrel distortion. Plus lens makes pincushion distortion.IncorrectB. Minus.
Minus lens makes barrel distortion. Plus lens makes pincushion distortion. -
Question 22 of 29
22. Question
You hand neutralize a lens and find no motion while using a +3.00 D trial lens with up and down motion. The you find no motion while suing a +5.00 D trial lens with side to side motion. What is the neutralizing power of the lens?
CorrectD. -3.00-2.00×090
IncorrectD. -3.00-2.00×090
-
Question 23 of 29
23. Question
A patient has read at six meters a standard Snellen letter labeled 20/40. Calculate the MAR.
CorrectB. 40/20= 2MAR
IncorrectB. 40/20= 2MAR
-
Question 24 of 29
24. Question
An optometrist has reduced the size of his projected chart to correspond to a testing distance of 15 ft. A patient needs to be 5 ft in front of the chart to be able to read the 20/400 letter. What is the actual acuity of this patient? (SELECT 3)
CorrectA.D.F. (15/5)(400)=20/1200=6/x
IncorrectA.D.F. (15/5)(400)=20/1200=6/x
-
Question 25 of 29
25. Question
When performing direct ophthalmoscopy which of the following is true?
CorrectC. Direct is erect and INdirect is INverted. Remember this mnemonic and you will get these questions right every time.
IncorrectC. Direct is erect and INdirect is INverted. Remember this mnemonic and you will get these questions right every time.
-
Question 26 of 29
26. Question
Which of the following diagnostic non contact lenses provides an erect virtual image of the fundus?
CorrectB. Hruby lens
IncorrectB. Hruby lens
-
Question 27 of 29
27. Question
You measure an Rx of +4.50-6.00×075 in a lensometer with a +25D standard badal lens. How far does the object move from its original primary position on the 165 meridian?
CorrectB. 2.4 further. -1.50=x25^2 x=-2.4mm
IncorrectB. 2.4 further. -1.50=x25^2 x=-2.4mm
-
Question 28 of 29
28. Question
Pantoscopic tilt of a spherical plus (+) lens induces a cyl. axis in which meridian? Face Form tilt of a spherical plus (+) lens induces a cyl. axis in which meridian? By cyl. axis we mean the axis of the spherocylinder in minus cyl. Notation.
CorrectA. 090:180. Plus lens induces plus cylinder on the axis. Panto induces on 180, faceform on 090. Since the answer has to be in minus cylinder form minus lens is induced on 090 for panto and faceform on 180.
IncorrectA. 090:180. Plus lens induces plus cylinder on the axis. Panto induces on 180, faceform on 090. Since the answer has to be in minus cylinder form minus lens is induced on 090 for panto and faceform on 180.
-
Question 29 of 29
29. Question
Referring to Direct ophthalmoscopy, which of the following statements is FALSE?
CorrectE. produces a virtual image. A DO produces a real image
IncorrectE. produces a virtual image. A DO produces a real image
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- Answered
- Review