NBEO® Part 1 Full Length Test #2 - Ocular Disease
Next
0 of 46 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
Information
|
Optometry Board Practice Test for the NBEO® Part 1 Test #2 – Ocular Disease This test is comprised of 46 items, which must be completed within 46 minutes. |
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Exam is loading ...
You must sign in or sign up to start the exam.
You have to finish following exam, to start this exam:
Results
0 of 46 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You answered 0 of 0 (0) questions correct
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Ocular Disease: Conjunctiva 0%
- Ocular Disease: Cornea 0%
- Ocular Disease: Cornea/Refractive Surgery 0%
- Ocular Disease: Episclera/Sclera/Anterior and Posterior Uvea 0%
- Ocular Disease: Glaucoma 0%
- Ocular Disease: Lens/Cataract/IOL Pre- and Post-op Care 0%
- Ocular Disease: Lids/Lashes/Lacrimal System 0%
- Ocular Disease: Neuro-Ophthalmic Disorder 0%
- Ocular Disease: Ocular Adnexa/Orbit/External Disease 0%
- Ocular Disease: Ocular Adnexa/Orbit/External Disease + Retina 0%
- Ocular Disease: Retina/Choroid 0%
- Ocular Disease: Trauma 0%
-
Based on your performance on this Optometry Board Part 1 Practice Test, you’re not yet ready for the NBEO® Part 1.
Keep your head up! Also, don’t focus on your estimated score, they mean essentially nothing at the start. Rarely does anyone start these exams and score well immediately, if that was the case then they wouldn’t even need to practice! These are ‘practice’ tests, meaning you’re practicing to improve your skills. If you continue to work hard and study, read and understand the solutions, practice with “OptometryBoards.com” daily and give it your best effort, we promise your score will improve. Review and learn for now, and the scores will come.
-The “OptometryBoards.com” Team
-
Congratulations! Based on your performance on this Optometry Board Part 1 Practice Test, you’re predicted to pass your NBEO® Part 1! Keep hammering away at our Optometry Board questions so that you can keep up the great work!
-The “OptometryBoards.com” Team
-
Question 1 of 46
1. Question
Patient comes in asking about wavefront- Guided Lasik. What are the benefits that this specific treatment provides compared to normal Lasik?
CorrectA. Wavefront provides less low level aberrations thus allowing the patient to achieve 20/20 without spectacle correction
IncorrectA. Wavefront provides less low level aberrations thus allowing the patient to achieve 20/20 without spectacle correction
-
Question 2 of 46
2. Question
Patient presents with the following topography. What layer of the cornea is most affected based off what you see?
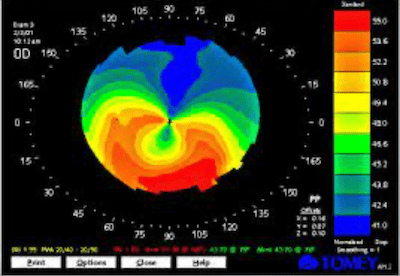 Correct
CorrectC. Corneal stroma thinning is affected in both Keratoconus and PMN. Note on the topography the red indicated corneal steeping and blue is corneal flattening.
IncorrectC. Corneal stroma thinning is affected in both Keratoconus and PMN. Note on the topography the red indicated corneal steeping and blue is corneal flattening.
-
Question 3 of 46
3. Question
Which of the following are not considered signs of keratoconus? (SELECT 3)
CorrectB,E,G. Ferry’s line is corneal epithelial iron deposits, Stocker’s line is caused by pterygium, Kayser- fleischer ring is caused by wilson’s disease
IncorrectB,E,G. Ferry’s line is corneal epithelial iron deposits, Stocker’s line is caused by pterygium, Kayser- fleischer ring is caused by wilson’s disease
-
Question 4 of 46
4. Question
All of the following would differentiate between Megalocornea and Buphthalmos EXCEPT:
CorrectC. Megalocornea is determined by corneal diameter of greater than 10mm, abnormal axial length, and can lead to congenital glaucoma.
IncorrectC. Megalocornea is determined by corneal diameter of greater than 10mm, abnormal axial length, and can lead to congenital glaucoma.
-
Question 5 of 46
5. Question
Which mirror of a goldmann gonioscopic lens would you use to view the posterior ora serrata?
CorrectD. 67 degree mirror. The more angled the mirror the more anterior the structure you will see. Trapezoid or 73 degree mirror is used to see the equator of the eye.
IncorrectD. 67 degree mirror. The more angled the mirror the more anterior the structure you will see. Trapezoid or 73 degree mirror is used to see the equator of the eye.
-
Question 6 of 46
6. Question
All of the following are diagnostic tests for glaucoma EXCEPT for:
CorrectD. Near visual acuity. Standard of care for glaucoma testing is goldmann tonometry for IOP, Humphrey visual field for any nerve damage analysis, Pachymetry in order to accurately adjust the IOP readings, Gonioscopy for determining if its closed angle or open angle glaucoma.
IncorrectD. Near visual acuity. Standard of care for glaucoma testing is goldmann tonometry for IOP, Humphrey visual field for any nerve damage analysis, Pachymetry in order to accurately adjust the IOP readings, Gonioscopy for determining if its closed angle or open angle glaucoma.
-
Question 7 of 46
7. Question
According to the Ocular hypertension treatment study (OHTS), which one of the following has a higher risk of developing glaucoma?
CorrectC. High IOP and thicker cornea. A thicker cornea will cause a falsely low IOP reading. A thinner cornea will cause a falsely high IOP. The higher the IOP is past 21mmHg the higher the likelihood the patient will have glaucoma.
IncorrectC. High IOP and thicker cornea. A thicker cornea will cause a falsely low IOP reading. A thinner cornea will cause a falsely high IOP. The higher the IOP is past 21mmHg the higher the likelihood the patient will have glaucoma.
-
Question 8 of 46
8. Question
Young male patient presents to your office with anisocoria. After examination, you find the following: Anisocoria is larger in dim illumination and accommodative response is increased. According to the information, which one of the following is the MOST probable cause of pupillary anomaly?
CorrectA. Horner’s syndrome. Patients pupils will have anisocoria with the ptotic eye having the smaller pupil. The anisocoria is more prominent in the dark, indicating pathology of the pupillary dilator. The smaller pupil takes a longer time to dilate when a bright source of light is moved away from the eye. This phenomenon is called dilation lag
IncorrectA. Horner’s syndrome. Patients pupils will have anisocoria with the ptotic eye having the smaller pupil. The anisocoria is more prominent in the dark, indicating pathology of the pupillary dilator. The smaller pupil takes a longer time to dilate when a bright source of light is moved away from the eye. This phenomenon is called dilation lag
-
Question 9 of 46
9. Question
Your patient presents with the following: AV nicking, Flame hemorrhages and cotton wool spots. According to Keith Wagener Barker’s hypertensive retinopathy classification, your patient can be classified as to be in stage___.
CorrectC. III. Grade 1: Mild, generalized constriction of retinal arterioles. Grade 2: Definite focal narrowing of retinal arterioles + AV nicking. Grade 3: Grade 2 + flame-shaped hemorrhages + cotton-wool spots + hard exudates. Grade 4: Severe Grade 3 retinopathy + papilledema or retinal edema.
IncorrectC. III. Grade 1: Mild, generalized constriction of retinal arterioles. Grade 2: Definite focal narrowing of retinal arterioles + AV nicking. Grade 3: Grade 2 + flame-shaped hemorrhages + cotton-wool spots + hard exudates. Grade 4: Severe Grade 3 retinopathy + papilledema or retinal edema.
-
Question 10 of 46
10. Question
Which of the following is the discussed likely secondary mechanism of damage in primary open angle glaucoma?
CorrectB. Glutamate cytotoxicity. Glaucoma is a disease of pressure irregulation leading to retinal necrosis. Glutamate is the eye’s excitatory neurotransmitter. As pressure on these nerves increases it will tend to over compensate for the lack of the signal transduction that occurs. Thus excess release of glutamate is a secondary issue that can cause damage to the nerves causing a glaucoma like damage.
IncorrectB. Glutamate cytotoxicity. Glaucoma is a disease of pressure irregulation leading to retinal necrosis. Glutamate is the eye’s excitatory neurotransmitter. As pressure on these nerves increases it will tend to over compensate for the lack of the signal transduction that occurs. Thus excess release of glutamate is a secondary issue that can cause damage to the nerves causing a glaucoma like damage.
-
Question 11 of 46
11. Question
All of the following are false regarding trachoma EXCEPT:
CorrectA. Trachoma is a disease of the eye caused by infection with the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
IncorrectA. Trachoma is a disease of the eye caused by infection with the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
-
Question 12 of 46
12. Question
Which of the following will not cause corneal verticillata?
CorrectD. Autosomal dominant skin condition. Corneal verticillata can be caused by chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, amiodarone ( RA drug), Indomethacin, Tamoxifen, Rho kinase inhibitors, and fabry’s disease.
IncorrectD. Autosomal dominant skin condition. Corneal verticillata can be caused by chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, amiodarone ( RA drug), Indomethacin, Tamoxifen, Rho kinase inhibitors, and fabry’s disease.
-
Question 13 of 46
13. Question
Which of the following is not associated with krukenberg spindles?
CorrectD. Anterior capsular stars have no association with krukenberg spindles. Lens cataracts can push on the iris and can be a secondary cause of krukenberg spindles. The most common cause is lens zonules rubbing against the back of the iris releasing pigment causing those spindles to form.
IncorrectD. Anterior capsular stars have no association with krukenberg spindles. Lens cataracts can push on the iris and can be a secondary cause of krukenberg spindles. The most common cause is lens zonules rubbing against the back of the iris releasing pigment causing those spindles to form.
-
Question 14 of 46
14. Question
All of the following would differentiate between megalocornea and buphthalmos EXCEPT?
CorrectC. length of vitreous. Megalocornea is a rare developmental defect characterized by nonprogressive, usually symmetric, bilateral enlargement of the diameter of the cornea ≥13 mm. Buphthalmos is used to describe the visible enlargement of the eyeball detected at birth or soon after, due to any uncontrolled glaucoma in early childhood.
IncorrectC. length of vitreous. Megalocornea is a rare developmental defect characterized by nonprogressive, usually symmetric, bilateral enlargement of the diameter of the cornea ≥13 mm. Buphthalmos is used to describe the visible enlargement of the eyeball detected at birth or soon after, due to any uncontrolled glaucoma in early childhood.
-
Question 15 of 46
15. Question
Which of the following is accurate for patients who has a central corneal nebula?
CorrectC. Nebular corneal opacity is a faint opacity which results due to superficial scars involving Bowman’s layer and superficial stroma.
IncorrectC. Nebular corneal opacity is a faint opacity which results due to superficial scars involving Bowman’s layer and superficial stroma.
-
Question 16 of 46
16. Question
Which of the following is MOST associated with dry eye disease?
CorrectA. Dry eye disease is directly linked to the lack of aqueous produced by the tear glands.
IncorrectA. Dry eye disease is directly linked to the lack of aqueous produced by the tear glands.
-
Question 17 of 46
17. Question
Which of the following is TRUE regarding Scleral chemical acid injury?
CorrectA. Acids = Coagulation/denaturation/precipitation of proteins. Alkali = Saponification of fatty acids within cell membranes
IncorrectA. Acids = Coagulation/denaturation/precipitation of proteins. Alkali = Saponification of fatty acids within cell membranes
-
Question 18 of 46
18. Question
Which of the following are most associated with Nanophthalmos? (SELECT 2)
CorrectA,B. nanophthalmos is caused by fetal alcohol syndrome, mucopolysaccharidosis, myotonic dystrophy, achondroplasia
IncorrectA,B. nanophthalmos is caused by fetal alcohol syndrome, mucopolysaccharidosis, myotonic dystrophy, achondroplasia
-
Question 19 of 46
19. Question
Which complication is MOST LIKELY expected after a YAG capsulotomy procedure?
CorrectA. Pupillary capture. YAG capsulotomy is the procedure of removing the capsular bag that is posterior to the IOL. Pupillary capture is an unusual complication of posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation and may occur in the early or late postoperative period
IncorrectA. Pupillary capture. YAG capsulotomy is the procedure of removing the capsular bag that is posterior to the IOL. Pupillary capture is an unusual complication of posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation and may occur in the early or late postoperative period
-
Question 20 of 46
20. Question
What type of collagen is the sclera primarily composed of?
CorrectA. Type 1. Human scleral tissue contains approximately 50% collagen by weight, consisting predominantly of type I collagen. There is little or no evidence for the presence of substantial quantities of type II, type III or other collagen types.
IncorrectA. Type 1. Human scleral tissue contains approximately 50% collagen by weight, consisting predominantly of type I collagen. There is little or no evidence for the presence of substantial quantities of type II, type III or other collagen types.
-
Question 21 of 46
21. Question
Which of the following is not an non-infectious cause of episcleritis?
CorrectD. The question is asking what is an infectious cause of episcleritis. Anything granulomatosis automatically means infectious with the exception of sarcoidosis.
IncorrectD. The question is asking what is an infectious cause of episcleritis. Anything granulomatosis automatically means infectious with the exception of sarcoidosis.
-
Question 22 of 46
22. Question
Which of the following is NOT true regarding Scleromalacia perforans?
CorrectC. Scleromalacia perforans is a rare, severe eye disorder developing an autoimmune damage of episcleral and scleral performing vessels.
IncorrectC. Scleromalacia perforans is a rare, severe eye disorder developing an autoimmune damage of episcleral and scleral performing vessels.
-
Question 23 of 46
23. Question
Which of the following is NOT true regarding Staphyloma of the Sclera?
CorrectD. Rapid neovascularization is present. Staphyloma of sclera present with no neovascularization. The sclera is avascular.
IncorrectD. Rapid neovascularization is present. Staphyloma of sclera present with no neovascularization. The sclera is avascular.
-
Question 24 of 46
24. Question
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding Hyaline Degeneration?
CorrectA. Hyaline degeneration occurs when smooth muscle is replaced by fibrous connective tissue and is the most common form of degeneration in leiomyomas. Patients do not present with uveitis, glaucoma, and keratitis when hyaline degeneration occurs.
IncorrectA. Hyaline degeneration occurs when smooth muscle is replaced by fibrous connective tissue and is the most common form of degeneration in leiomyomas. Patients do not present with uveitis, glaucoma, and keratitis when hyaline degeneration occurs.
-
Question 25 of 46
25. Question
Which of the following structures is responsible for maintaining intraocular pressure?
CorrectB. Ciliary muscle when stimulated will pull on the scleral spur thus opening the Uveal scleral outflow pathway
IncorrectB. Ciliary muscle when stimulated will pull on the scleral spur thus opening the Uveal scleral outflow pathway
-
Question 26 of 46
26. Question
Which of the following is NOT associated with Scleral Injury due to trauma?
CorrectD. Scleral injury cause a decrease in IOP not an increase in IOP
IncorrectD. Scleral injury cause a decrease in IOP not an increase in IOP
-
Question 27 of 46
27. Question
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Aniridia?
CorrectE. Aniridia is a loss or lack of iris. Synechia will only present when an iris is present.
IncorrectE. Aniridia is a loss or lack of iris. Synechia will only present when an iris is present.
-
Question 28 of 46
28. Question
Plano patient stares at an object located at optical infinity. What is the dioptric power of the cornea in this patient?
CorrectD. 40. The eye total has 60 Diopters of power. Cornea contributes 40D, and the lens contributes 20D.
IncorrectD. 40. The eye total has 60 Diopters of power. Cornea contributes 40D, and the lens contributes 20D.
-
Question 29 of 46
29. Question
What laser is used to reshape the cornea in LASIK?
CorrectC. Excimer laser is used to reshape the cornea thus resulting in correction of refractive error. Femtosecond laser is used to create the flap in LASIK
IncorrectC. Excimer laser is used to reshape the cornea thus resulting in correction of refractive error. Femtosecond laser is used to create the flap in LASIK
-
Question 30 of 46
30. Question
Which purkinje image is used for keratometry readings?
CorrectB. Purkinje image 1 is a direct result of reflection from the anterior corneal surface. When we do keratometry we are measuring the shape of the anterior cornea to see how to fit a RGP properly on that surface.
IncorrectB. Purkinje image 1 is a direct result of reflection from the anterior corneal surface. When we do keratometry we are measuring the shape of the anterior cornea to see how to fit a RGP properly on that surface.
-
Question 31 of 46
31. Question
What is the female equivalent to maturation and storage of reproductive chromosomes gametes found in male testes?
CorrectB. Ovaries are where female gametes are stored (eggs).
IncorrectB. Ovaries are where female gametes are stored (eggs).
-
Question 32 of 46
32. Question
What layer of the retina does the photoreceptor body found in?
CorrectA. ONL. The photoreceptor receives its signal from the RPE so the OS portion of the photoreceptor is like a dendrite and collects the photon. Interpretation occurs where a nucleus is present. ONL is the first layer of nuclear location in the retina.
IncorrectA. ONL. The photoreceptor receives its signal from the RPE so the OS portion of the photoreceptor is like a dendrite and collects the photon. Interpretation occurs where a nucleus is present. ONL is the first layer of nuclear location in the retina.
-
Question 33 of 46
33. Question
What is the most common side effect of netarsudil?
CorrectA. Redness of the conjunctiva is the most commonly reported side effect of netarsudil AKA Rhopressa. This is due to the fact that there are rho kinase receptors found on blood vessels. Rhopressa is an inhibitor of rho kinase which causes vasodilation of the blood vessels.
IncorrectA. Redness of the conjunctiva is the most commonly reported side effect of netarsudil AKA Rhopressa. This is due to the fact that there are rho kinase receptors found on blood vessels. Rhopressa is an inhibitor of rho kinase which causes vasodilation of the blood vessels.
-
Question 34 of 46
34. Question
According to the OATS study which of the following treatment options was shown to reduce chances of glaucoma progression?
CorrectA. Topical ocular hypotensive medications such as latanoprost was affected in delay or prevent POAG individual with elevated IOP by 30% once IOP pressure was between 24 and 32 mm Hg
IncorrectA. Topical ocular hypotensive medications such as latanoprost was affected in delay or prevent POAG individual with elevated IOP by 30% once IOP pressure was between 24 and 32 mm Hg
-
Question 35 of 46
35. Question
Which of the following medications is best known to treat myokymia?
CorrectB. Zyrtec is a second generation antihistamine that has an off label treatment for eyelid myokymia. However there is no understanding to why this works.
IncorrectB. Zyrtec is a second generation antihistamine that has an off label treatment for eyelid myokymia. However there is no understanding to why this works.
-
Question 36 of 46
36. Question
What is the net movement of ions in the cornea during corneal deturgescence?
CorrectB. K is actively outside on the tear film and moves into the stroma to the aqueous humor. As this happens Na passively enters epithelial cells from the tear film
IncorrectB. K is actively outside on the tear film and moves into the stroma to the aqueous humor. As this happens Na passively enters epithelial cells from the tear film
-
Question 37 of 46
37. Question
What is the MOST common systemic condition that causes posterior uveitis?
CorrectA. Toxoplasmosis is more commonly found systematically than sarcoidosis. All options do cause posterior uveitis. Syphilis rarely causes posterior uveitis.
IncorrectA. Toxoplasmosis is more commonly found systematically than sarcoidosis. All options do cause posterior uveitis. Syphilis rarely causes posterior uveitis.
-
Question 38 of 46
38. Question
Which of the following bones do not make up the medial wall of the orbital?
CorrectE. Together, the zygomatic bone makes up the lateral wall of the orbit with the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. Remember SMEL my medial wall → sphenoid, maxillary, ethmoid, lacrimal.
IncorrectE. Together, the zygomatic bone makes up the lateral wall of the orbit with the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. Remember SMEL my medial wall → sphenoid, maxillary, ethmoid, lacrimal.
-
Question 39 of 46
39. Question
What test is adequate enough to evaluate the health of nasociliary nerves ability to initiate a response to a stimulus?
CorrectA. The cotton swab test is used to evaluate corneal sensitivity, specifically cranial nerve V1, the nasociliary branch off of the ophthalmic nerve.
IncorrectA. The cotton swab test is used to evaluate corneal sensitivity, specifically cranial nerve V1, the nasociliary branch off of the ophthalmic nerve.
-
Question 40 of 46
40. Question
Which of the following follows the jones and wobig lacrimal pump theory
CorrectB. Blinking occurs from lateral to medial canthus and helps to move tears towards the puncta. The puncta under open conditions collect the tears through capillary attraction method
IncorrectB. Blinking occurs from lateral to medial canthus and helps to move tears towards the puncta. The puncta under open conditions collect the tears through capillary attraction method
-
Question 41 of 46
41. Question
Which of the following are not functions of the tear film?
CorrectD. The glands of wolfring are located in the tarsal conjunctiva and are assistant lacrimal glands along with the glands of Kruse that provide aqueous layer to the tear film.
IncorrectD. The glands of wolfring are located in the tarsal conjunctiva and are assistant lacrimal glands along with the glands of Kruse that provide aqueous layer to the tear film.
-
Question 42 of 46
42. Question
What is the main stimulator for mucous secretions in the conjunctival epithelium?
CorrectB. parasympathetic nerve endings surround goblet cells and cause increase in mucous secretions
IncorrectB. parasympathetic nerve endings surround goblet cells and cause increase in mucous secretions
-
Question 43 of 46
43. Question
Which of the following diseases are directly caused by a ABCA4 mutation?
CorrectA. Stargardt’s disease is directly caused by a mutation in the ABCA4 membrane protein and is responsible for moving all trans retinal from the photoreceptor to the cytoplasm
IncorrectA. Stargardt’s disease is directly caused by a mutation in the ABCA4 membrane protein and is responsible for moving all trans retinal from the photoreceptor to the cytoplasm
-
Question 44 of 46
44. Question
Goldmann tonometry is based on the Imbert fick law and treats all corneas to have an average thickness of 520um. What is the Imbert Fick Law?
CorrectB. Pressure inside is set to a infinite thin and covered by thin membrane is equal to the force necessary to flatten the sphere of the corneal shape
IncorrectB. Pressure inside is set to a infinite thin and covered by thin membrane is equal to the force necessary to flatten the sphere of the corneal shape
-
Question 45 of 46
45. Question
What is considered the average IOP value in a healthy patient younger than 50?
CorrectC. 15.5 mm Hg is the average IOP found in non glaucoma patients under the age of 50.
IncorrectC. 15.5 mm Hg is the average IOP found in non glaucoma patients under the age of 50.
-
Question 46 of 46
46. Question
Which condition can present with unilateral anterior uveitis?
CorrectC. Posner Schlossman Syndrome, also known as glaucomatocyclitis crisis, presents as an acute unilateral nongranulomatous anterior uveitis due to inflammation in the trabecular meshwork. These episodes are recurring and self-limiting each time and with the slit lamp biomicroscope, the practitioner will be able to see fine keratic precipitates. In addition herpes and Fuch’s Heterochromic Iridocyclitis result in a unilateral chronic non-granulomatous anterior uveitis.
Any type of systemic condition would result in a bilateral uveitis. Keep in mind the ones to cause a chronic granulomatous anterior uveitis include sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, syphilis, lyme disease and herpes amongst others. All five of these conditions may also result in a panuveitis and/or posterior uveitis.
IncorrectC. Posner Schlossman Syndrome, also known as glaucomatocyclitis crisis, presents as an acute unilateral nongranulomatous anterior uveitis due to inflammation in the trabecular meshwork. These episodes are recurring and self-limiting each time and with the slit lamp biomicroscope, the practitioner will be able to see fine keratic precipitates. In addition herpes and Fuch’s Heterochromic Iridocyclitis result in a unilateral chronic non-granulomatous anterior uveitis.
Any type of systemic condition would result in a bilateral uveitis. Keep in mind the ones to cause a chronic granulomatous anterior uveitis include sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, syphilis, lyme disease and herpes amongst others. All five of these conditions may also result in a panuveitis and/or posterior uveitis.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- Answered
- Review