NBEO® Part 1 Full Length Test #2 - Neuroanatomy
Next
0 of 21 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
Information
|
Optometry Board Practice Test for the NBEO® Part 1 Test #2 – Neuroanatomy This test is comprised of 21 items with 21 minutes to finish. |
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Exam is loading ...
You must sign in or sign up to start the exam.
You have to finish following exam, to start this exam:
Results
0 of 21 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You answered 0 of 0 (0) questions correct
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Neuroanatomy 0%
- Neuroscience: Neuroanatomy 0%
-
Based on your performance on this Optometry Board Part 1 Practice Test, you’re not yet ready for the NBEO® Part 1.
Keep your head up! Also, don’t focus on your estimated score, they mean essentially nothing at the start. Rarely does anyone start these exams and score well immediately, if that was the case then they wouldn’t even need to practice! These are ‘practice’ tests, meaning you’re practicing to improve your skills. If you continue to work hard and study, read and understand the solutions, practice with “OptometryBoards.com” daily and give it your best effort, we promise your score will improve. Review and learn for now, and the scores will come.
-The “OptometryBoards.com” Team
-
Congratulations! Based on your performance on this Optometry Board Part 1 Practice Test, you’re predicted to pass your NBEO® Part 1! Keep hammering away at our Optometry Board questions so that you can keep up the great work!
-The “OptometryBoards.com” Team
-
Question 1 of 21
1. Question
What structure provides neurological support to the central nervous system?
CorrectA. Oligodendrocytes are the myelinating cells of the CNS that enable fast saltatory impulse propagation. Schwann Cells are myelinating cells of the PNS that provide the same function of the Oligodendrocytes but only to the PNS. Altho oligodendrocytes are a type of glial cells, the answer is not specific to only the CNS. Astrocytes are a sub type of glial cell that are star shaped and process envelope synapse made by the neuron.
IncorrectA. Oligodendrocytes are the myelinating cells of the CNS that enable fast saltatory impulse propagation. Schwann Cells are myelinating cells of the PNS that provide the same function of the Oligodendrocytes but only to the PNS. Altho oligodendrocytes are a type of glial cells, the answer is not specific to only the CNS. Astrocytes are a sub type of glial cell that are star shaped and process envelope synapse made by the neuron.
-
Question 2 of 21
2. Question
A divergent neuronal circuit is defined as one in which?
CorrectB. A neural circuit is a group of neurons in which impulse is affected at the same time usually in the same direction. Convergent means many neurons send a signal to one nerve. Divergent means one nerve sends a signal to several nerves.
IncorrectB. A neural circuit is a group of neurons in which impulse is affected at the same time usually in the same direction. Convergent means many neurons send a signal to one nerve. Divergent means one nerve sends a signal to several nerves.
-
Question 3 of 21
3. Question
Which of the following is true for nerve impulse conduction?
CorrectB. nerve impulses are regulated by myelination of the axons. The more myelination a nerve has the slower the impulse. Continuous condition is slower due to the fact that the nerve undergoes a repolarization phase that lasts longer than a non continuous conduction.
IncorrectB. nerve impulses are regulated by myelination of the axons. The more myelination a nerve has the slower the impulse. Continuous condition is slower due to the fact that the nerve undergoes a repolarization phase that lasts longer than a non continuous conduction.
-
Question 4 of 21
4. Question
Interstitial fluid is accumulated in all of the following sites, EXCEPT?
CorrectA. Cerebrospinal fluid. Interstitial fluid is fluid found within the space around a cell. It comes from blood vessel leakage. Cerebrospinal fluid is colorless fluid produced by the spinal cord that surrounds the CNS not space around cells.
IncorrectA. Cerebrospinal fluid. Interstitial fluid is fluid found within the space around a cell. It comes from blood vessel leakage. Cerebrospinal fluid is colorless fluid produced by the spinal cord that surrounds the CNS not space around cells.
-
Question 5 of 21
5. Question
During the event identified by number 2, which of the following molecular events is occurring?
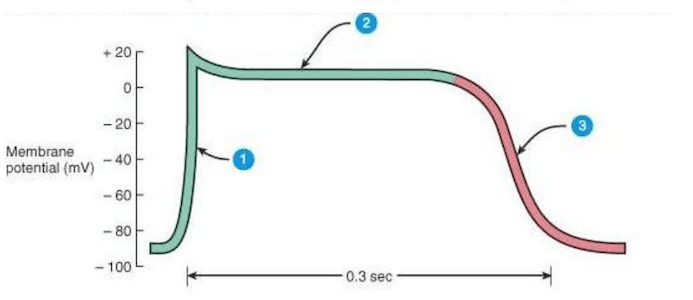 Correct
CorrectB. 1) opening of Na+ channels 2) opening of calcium channels 3) Calcium channels inactivated and potassium flow out
IncorrectB. 1) opening of Na+ channels 2) opening of calcium channels 3) Calcium channels inactivated and potassium flow out
-
Question 6 of 21
6. Question
This electrical event triggers contraction of the atria.
CorrectD. P wave. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart.
IncorrectD. P wave. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart.
-
Question 7 of 21
7. Question
Which of the following structures is considered the pacemaker of the heart?
CorrectA. SA node is the start node.
IncorrectA. SA node is the start node.
-
Question 8 of 21
8. Question
If a patient has paralysis of cranial nerve IV, then which of the following is the most likely outcome?
CorrectA. Intorsion of the eye. CN4 innervates the SO. The SO primary function is intorsion
IncorrectA. Intorsion of the eye. CN4 innervates the SO. The SO primary function is intorsion
-
Question 9 of 21
9. Question
Damage of which of the following cranial nerves leads to anosmia?
CorrectB. CN2 innervates smell. Anosmia is the loss of smell
IncorrectB. CN2 innervates smell. Anosmia is the loss of smell
-
Question 10 of 21
10. Question
What part of the brain is Brodmann area 8 located in?
CorrectD. Frontal. Brodmann area 8 is the area involved in the management of uncertainty. Clinically if a patient comes in uncertain about everything and a saccadic defect. Then we can localize what area of the brain is affected.
IncorrectD. Frontal. Brodmann area 8 is the area involved in the management of uncertainty. Clinically if a patient comes in uncertain about everything and a saccadic defect. Then we can localize what area of the brain is affected.
-
Question 11 of 21
11. Question
Which part of the ear is controlled by linear VOR?
CorrectC. Vestibule is controlled by linear VOR. Semicircular canals are controlled by angular VOR
IncorrectC. Vestibule is controlled by linear VOR. Semicircular canals are controlled by angular VOR
-
Question 12 of 21
12. Question
What part of the brain is considered the control center for vergences?
CorrectB. Midbrain. local circuit neurons located in the midbrain near the oculomotor nucleus. These neurons generate a burst of action potentials. The onset of the burst is the command to generate a vergence movement, and the frequency of the burst determines its velocity
IncorrectB. Midbrain. local circuit neurons located in the midbrain near the oculomotor nucleus. These neurons generate a burst of action potentials. The onset of the burst is the command to generate a vergence movement, and the frequency of the burst determines its velocity
-
Question 13 of 21
13. Question
A lesion above the left side of the medulla will lead to what problems with motor control?
CorrectA. A lesion above the medulla will lead to problems with motor control on the contralateral side of the upper body not the upper face. The facial muscles are controlled by the facial nerve found in the upper brain
IncorrectA. A lesion above the medulla will lead to problems with motor control on the contralateral side of the upper body not the upper face. The facial muscles are controlled by the facial nerve found in the upper brain
-
Question 14 of 21
14. Question
Which of the following makes up the internal capsule in the forebrain?
CorrectA. Pyramidal motor cell axons come together and form the internal capsule. These fibers then move through the cerebral peduncles, pons and medulla to from the medulla pyramids
IncorrectA. Pyramidal motor cell axons come together and form the internal capsule. These fibers then move through the cerebral peduncles, pons and medulla to from the medulla pyramids
-
Question 15 of 21
15. Question
What pathway carries pain and temperature information from the body?
CorrectB. anterolateral system AKA spinothalamic pathway carries pain and temperature information from the body. Trigeminothalamic pathway carries pain and temperature information from the face.
IncorrectB. anterolateral system AKA spinothalamic pathway carries pain and temperature information from the body. Trigeminothalamic pathway carries pain and temperature information from the face.
-
Question 16 of 21
16. Question
Which of the following are controlled by the autonomic nervous system? (SELECT TWO)
CorrectC and D. The autonomic nervous system is composed of neurons that control input of the visceral organs, secretory glands, and smooth muscles. However, the autonomic nervous system is not a voluntary input system. Such examples of these would be the first two options listed.
IncorrectC and D. The autonomic nervous system is composed of neurons that control input of the visceral organs, secretory glands, and smooth muscles. However, the autonomic nervous system is not a voluntary input system. Such examples of these would be the first two options listed.
-
Question 17 of 21
17. Question
Which of the following LGN layers is located between each of the 6 layers of the LGN?
CorrectC. Koniocellular layers are located between each of the 6 layers throughout the LGN. The magnocellular layers are layers 1 and 2 on the ventral side of the LGN. Parvocellular layers are 3,4,5,6 on the dorsal side of the LGN.
IncorrectC. Koniocellular layers are located between each of the 6 layers throughout the LGN. The magnocellular layers are layers 1 and 2 on the ventral side of the LGN. Parvocellular layers are 3,4,5,6 on the dorsal side of the LGN.
-
Question 18 of 21
18. Question
Which receptive fields of the LGN respond to blue-yellow contrast?
CorrectC. Konio cells. Magno cells are sensitive to fast movements and large details. Parvo cells are sensitive to red green and fine details.
IncorrectC. Konio cells. Magno cells are sensitive to fast movements and large details. Parvo cells are sensitive to red green and fine details.
-
Question 19 of 21
19. Question
A 34 year old female is having issues determining the edge and color of an object. The patient was diagnosed with a tumor found pressing on the LGN. What cells in the LGN are directly affected in this patient and what layer are these cells mostly found?
CorrectD. simple cells are located in layer 4 of the LGN. Simple cells have elongated center surround receptive fields that respond to specific orientation, edge, color and depth.
IncorrectD. simple cells are located in layer 4 of the LGN. Simple cells have elongated center surround receptive fields that respond to specific orientation, edge, color and depth.
-
Question 20 of 21
20. Question
Which nucleus forms the tectotegmental tract?
CorrectB.The Edinger Westphal nucleus contains fibers that form the tectotegmental tract. The pretectal nucleus is not part of this tract. Pay close attention to the wording of this question. The tectotegmental tract is defined as the pretectal fibers projecting to both ipsilateral and contralateral edinger-westphal nuclei.
IncorrectB.The Edinger Westphal nucleus contains fibers that form the tectotegmental tract. The pretectal nucleus is not part of this tract. Pay close attention to the wording of this question. The tectotegmental tract is defined as the pretectal fibers projecting to both ipsilateral and contralateral edinger-westphal nuclei.
-
Question 21 of 21
21. Question
What artery supplies the frontal lobe of the brain?
CorrectE. Anterior cerebral and middle cerebral supplies the frontal lobe of the brain. Middle cerebral supplies blood to every part of the brain. The posterior cerebral supplies blood to the temporal and occipital lobes of the brain .
IncorrectE. Anterior cerebral and middle cerebral supplies the frontal lobe of the brain. Middle cerebral supplies blood to every part of the brain. The posterior cerebral supplies blood to the temporal and occipital lobes of the brain .
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- Answered
- Review